Computer-Science-A-level-Ocr
-
3-3-networks8 主题
-
3-2-databases7 主题
-
3-1-compression-encryption-and-hashing4 主题
-
2-5-object-oriented-languages7 主题
-
2-4-types-of-programming-language4 主题
-
2-3-software-development5 主题
-
2-2-applications-generation6 主题
-
2-1-systems-software8 主题
-
1-3-input-output-and-storage2 主题
-
1-2-types-of-processor3 主题
-
1-1-structure-and-function-of-the-processor1 主题
-
structuring-your-responses3 主题
-
the-exam-papers2 主题
-
8-2-algorithms-for-the-main-data-structures4 主题
-
8-1-algorithms10 主题
-
7-2-computational-methods11 主题
-
7-1-programming-techniques14 主题
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
entity-relationship-diagrams
-
data-normalisation
-
relational-databases
-
hashing
-
symmetric-vs-asymmetric-encryption
-
run-length-encoding-and-dictionary-coding
-
lossy-and-lossless-compression
-
polymorphism-oop
-
encapsulation-oop
-
inheritance-oop
-
attributes-oop
-
methods-oop
-
objects-oop
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
6-5-thinking-concurrently2 主题
-
6-4-thinking-logically2 主题
-
6-3-thinking-procedurally3 主题
-
6-2-thinking-ahead1 主题
-
6-1-thinking-abstractly3 主题
-
5-2-moral-and-ethical-issues9 主题
-
5-1-computing-related-legislation4 主题
-
4-3-boolean-algebra5 主题
-
4-2-data-structures10 主题
-
4-1-data-types9 主题
-
3-4-web-technologies16 主题
-
environmental-effects
-
automated-decision-making
-
computers-in-the-workforce
-
layout-colour-paradigms-and-character-sets
-
piracy-and-offensive-communications
-
analysing-personal-information
-
monitoring-behaviour
-
censorship-and-the-internet
-
artificial-intelligence
-
the-regulation-of-investigatory-powers-act-2000
-
the-copyright-design-and-patents-act-1988
-
the-computer-misuse-act-1990
-
the-data-protection-act-1998
-
adder-circuits
-
flip-flop-circuits
-
simplifying-boolean-algebra
-
environmental-effects
iteration
Iteration
What is iteration?
-
Iteration is the process of doing something more than once (repeat), otherwise known as a loop
-
A loop can be count controlled which means the code is repeated a fixed number of times
-
A loop can also be condition controlled which means the code is repeated until a condition is met
-
Three common loops are:
-
for loops (count controlled)
-
while loops (condition controlled)
-
do while loops (condition controlled)
-
For Loops
-
A
forloop is a count controlled loop that will repeat a fixed number of times. It provides a concise and structured way to perform repetitive tasks.
Syntax of a for loop
The syntax of a for loop consists of three main parts:
01 for i = x to y02 // Code to be executed in each iteration03 next i
-
Initialisation: The initialisation is executed only once at the beginning of the loop. It is used to initialise a counter variable that controls the loop’s execution which is
iin this example -
Range: The range that the count variable will increment through
-
Increment/Decrement: The default is to increment by 1 each time unless specified
Pseudocode example
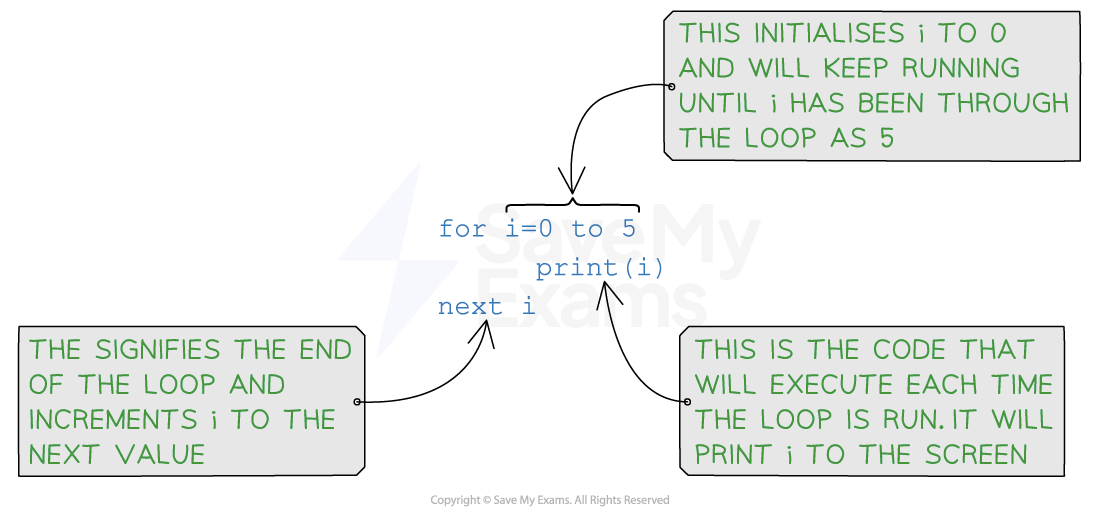
for loop example pseudocode
Python example
01 for i in range(0,6):02 print i
In Python, the range specifies the numbers used in the loop. The final number (6 in this case) is 1 higher than the number we want to run the loop with.
Java example
01 for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {02 System.out.println(i);03 }
Iterating over an array
Pseudocode example

for loop iterating over an array and outputting each item
Python example
01 fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"]02 for i in range(len(fruits)):03 print(fruits[i])
Java example
01 String[] fruits = {"apple", "banana", "orange"};02 for (int i = 0; i < fruits.length; i++) {03 System.out.println(fruits[i]);04 }
While Loops
-
A
whileloop is a condition controlled loop that will repeat until a condition is met -
Whileloops provide a flexible and powerful way to handle situations where the number of iterations is unknown in advance
Syntax of a while loop
-
The syntax of a
whileloop consists of a condition and a code block:
01 while condition02 // Code to be executed as long as the condition is true03 endwhile
-
The condition is evaluated before each iteration. If the condition evaluates to
true, the code block is executed -
If the condition evaluates to
false, the loop terminates.
Pseudocode example
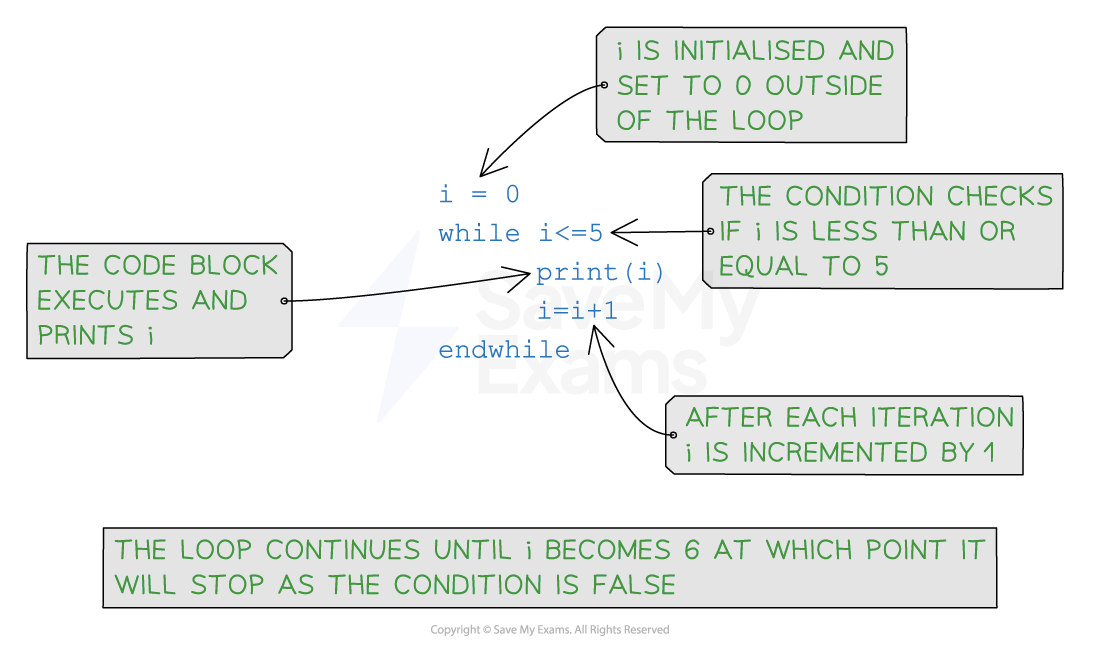
while loop example pseudocode
Python example
01 i = 002 while i <= 5:03 print(i)04 i = i + 1
Java example
01 int i = 0;02 while (i <= 5) {03 System.out.println(i);04 i = i + 1;05 }
Checking if the password is ‘secret’
Pseudocode example

while loop checking if the password is correct
Python example
01 password = ""02 while password != "secret":03 password = input("What is the password? ")
Java example
01 import java.util.Scanner;02 public class Main {03 public static void main(String[] args) {04 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);05 String password = "";06 while (!password.equals("secret")) {07 System.out.print("What is the password? ");08 password = scanner.nextLine();09 }10 scanner.close();11 }12 }
Examiner Tips and Tricks
-
Incrementing a variable can be done in different ways (depending on the language)
-
For example:
-
i= i + 1
-
i + = 1
-
i++
-
Worked Example
A simple Python program is shown below.01 //Program to calculate the number of times a number goes into 1000203 count = 004 num = int(input("Enter a number"))05 while (count*num)<=10006 count=count+107 endwhile08 count=count-1 //Take one off as gone over09 print(str(num) + " goes into 100 " + str(count) + " times.")
State the output of the program when the number 30 is entered.
[1]
How to answer this question:
-
If 30 is entered this is saved in the variable
num -
The
whileloop will run whilecount*numis less than or equal to 100 -
countis 0, so 30 * 0 = 0 -
As there is a loop to iterate through it would be useful to produce a trace table to help us keep track of the value of the different variables
|
count |
num |
count * num |
|
0 |
30 |
|
|
1 |
|
30 |
|
2 |
|
60 |
|
3 |
|
90 |
|
4 |
|
120 |
|
3 |
|
|
-
The loop will repeat and when
countis 4,count*numis 120 which causes the condition to be false and the loop to stop -
Count is decremented
-
The statement which is printed is 30 goes into 100 3 times
Answer:
30 goes into 100 3 times.
Do While Loops
-
A
do whileloop is another example of a condition controlled loop that will repeat until a condition is met. -
Do whileloops provide a variation of thewhileloop with a slightly different behaviour -
The code within a
do whileloop will always run at least once, unlike awhileloop which may not run at all if the condition is already met
Syntax of a do while loop
-
The syntax of a
do whileloop consists of a code block and a condition:
01 do02

Responses