Computer-Science-A-level-Ocr
-
3-3-networks8 主题
-
3-2-databases7 主题
-
3-1-compression-encryption-and-hashing4 主题
-
2-5-object-oriented-languages7 主题
-
2-4-types-of-programming-language4 主题
-
2-3-software-development5 主题
-
2-2-applications-generation6 主题
-
2-1-systems-software8 主题
-
1-3-input-output-and-storage2 主题
-
1-2-types-of-processor3 主题
-
1-1-structure-and-function-of-the-processor1 主题
-
structuring-your-responses3 主题
-
the-exam-papers2 主题
-
8-2-algorithms-for-the-main-data-structures4 主题
-
8-1-algorithms10 主题
-
7-2-computational-methods11 主题
-
7-1-programming-techniques14 主题
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
entity-relationship-diagrams
-
data-normalisation
-
relational-databases
-
hashing
-
symmetric-vs-asymmetric-encryption
-
run-length-encoding-and-dictionary-coding
-
lossy-and-lossless-compression
-
polymorphism-oop
-
encapsulation-oop
-
inheritance-oop
-
attributes-oop
-
methods-oop
-
objects-oop
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
6-5-thinking-concurrently2 主题
-
6-4-thinking-logically2 主题
-
6-3-thinking-procedurally3 主题
-
6-2-thinking-ahead1 主题
-
6-1-thinking-abstractly3 主题
-
5-2-moral-and-ethical-issues9 主题
-
5-1-computing-related-legislation4 主题
-
4-3-boolean-algebra5 主题
-
4-2-data-structures10 主题
-
4-1-data-types9 主题
-
3-4-web-technologies16 主题
-
environmental-effects
-
automated-decision-making
-
computers-in-the-workforce
-
layout-colour-paradigms-and-character-sets
-
piracy-and-offensive-communications
-
analysing-personal-information
-
monitoring-behaviour
-
censorship-and-the-internet
-
artificial-intelligence
-
the-regulation-of-investigatory-powers-act-2000
-
the-copyright-design-and-patents-act-1988
-
the-computer-misuse-act-1990
-
the-data-protection-act-1998
-
adder-circuits
-
flip-flop-circuits
-
simplifying-boolean-algebra
-
environmental-effects
quick-sort
Quick sort
What is a quick sort?
-
A quick sort is another example of a divide and conquer algorithm that reduces the size of the problem into smaller problems that are more easily solvable by an algorithm
-
Below is an illustration of the quick sort

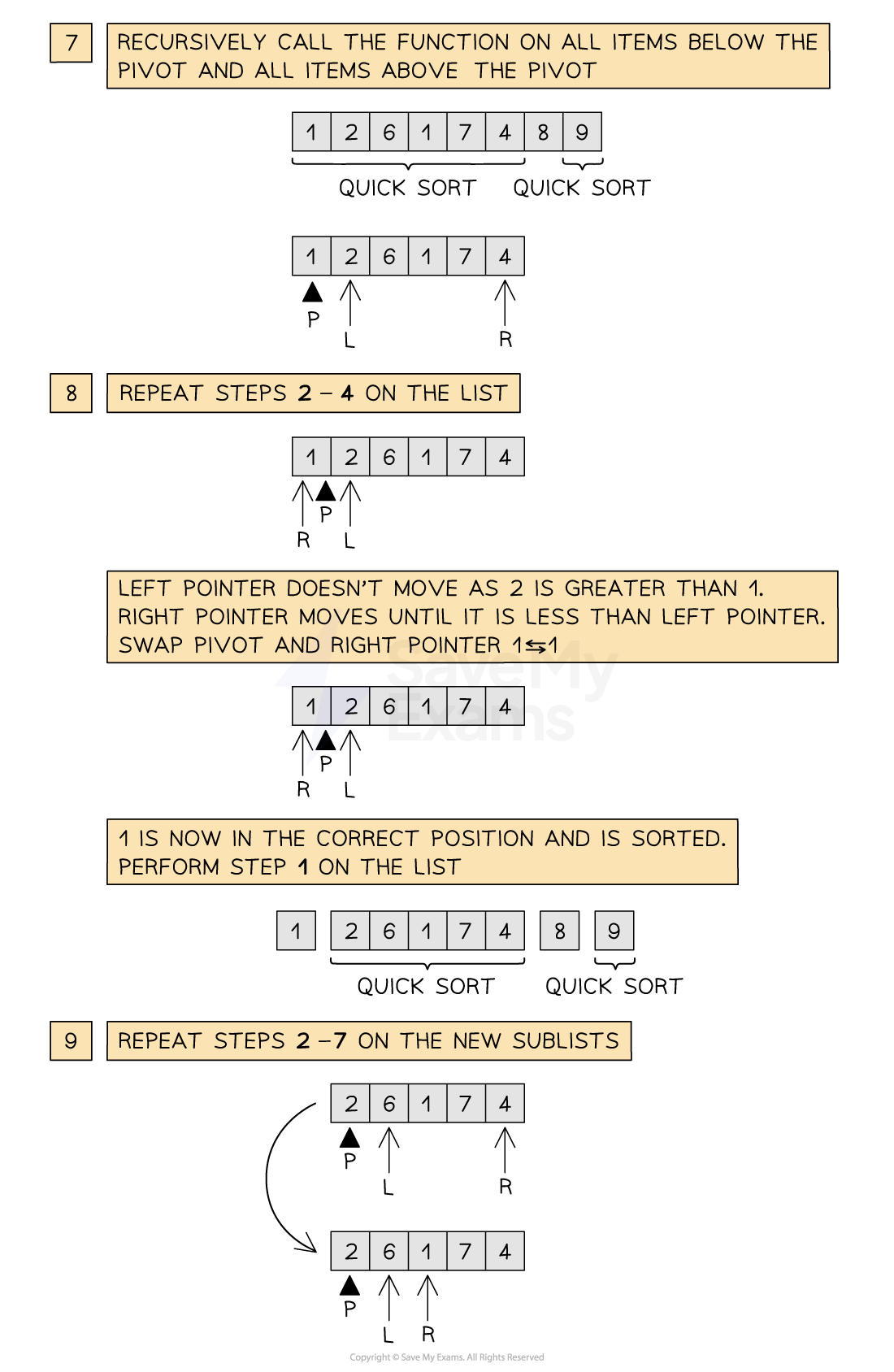
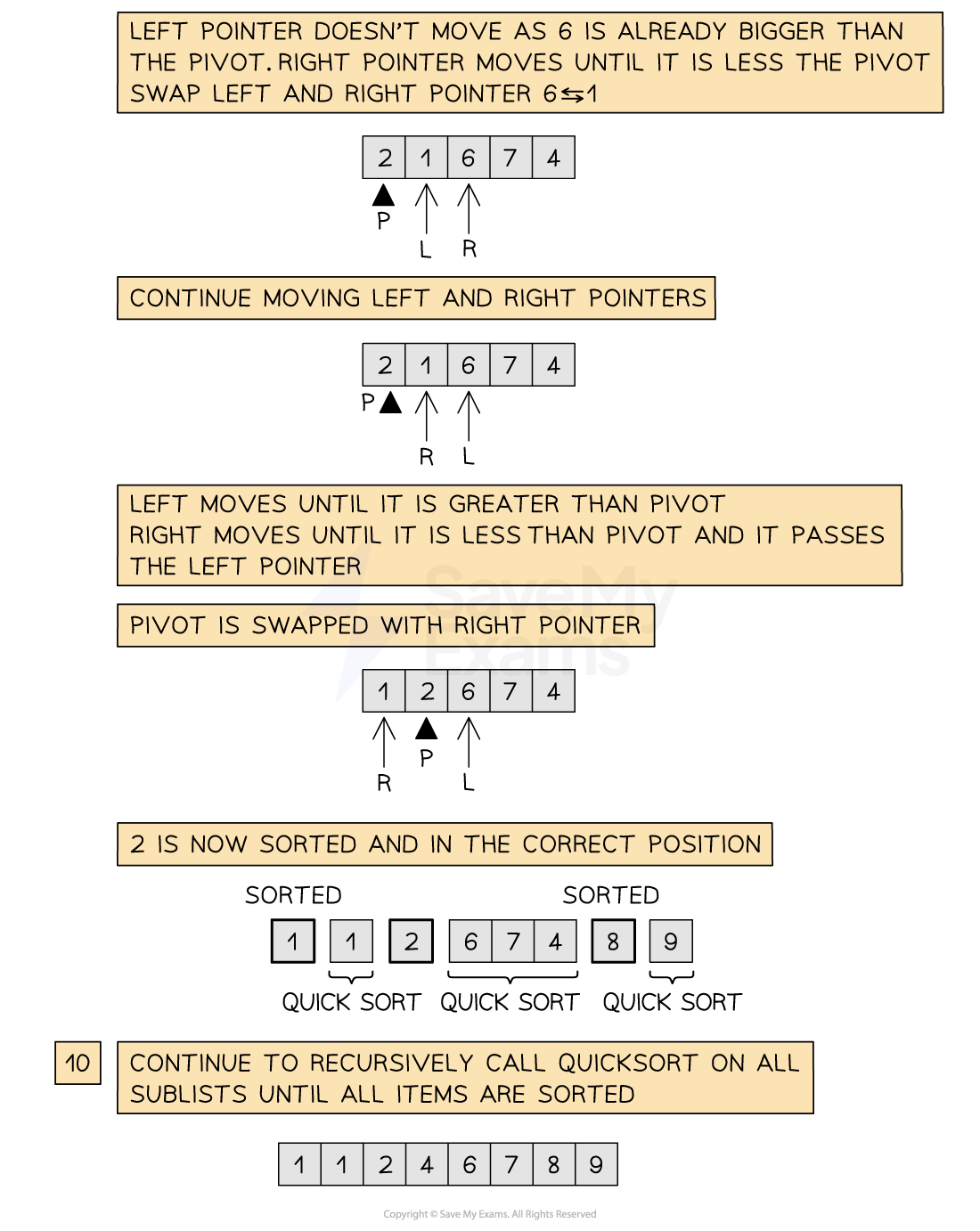
Figure 2: Performing the Quick sort
Time complexity of quick sort
-
Quick sort is a divide and conquer algorithm that splits the problem into smaller subproblems using a pivot value
-
The pivot divides the list into two parts: values less than the pivot and values greater than the pivot
-
Each sub list is then sorted recursively until the list is completely ordered
Best and average case
-
If the pivot divides the list roughly in the middle, the algorithm performs efficiently
-
Each level of recursion performs n operations to partition the list
-
There are approximately log n levels of recursion
-
This gives a best and average case time complexity of O(n log n)
Worst case
-
If the pivot is consistently placed at one extreme (for example, always the smallest or largest value), one partition becomes empty
-
This causes the recursion to degenerate into a single chain of calls
-
Each recursive call processes n – 1 elements, leading to n × (n – 1) operations, or O(n²) overall
-
Poor pivot selection or already sorted input data can lead to this worst-case scenario
-
In practice, randomised or median-of-three pivot selection is used to avoid the worst case
-
If recursion depth becomes too large, a stack overflow can occur due to too many recursive calls
Space complexity of a quick sort
-
Quick sort requires additional memory as copies of lists are made and put on the stack. The overall space complexity is therefore O(n) with O(n) additional space required
Tracing a quick sort
-
The trace table below shows the process of calling the quick sort and moving the left and right pointers up and down the list to find elements to swap and then find the correct position of the pivot
-
Once the pivot is in place, quick sort is recursively called on both sublists on either side of the pivot. Note that a second call to quick sort may not exist if the pivot value ends on either extreme of the list
-
The process repeats, calling quick sort on progressively smaller sublists until all values are in the correct order
Trace Table for the Quick sort
|
list |
operation |
done |
pivot |
list[pivot] |
left |
list[left] |
right |
list[right] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
[8, 2, 6, 1, 7, 9, 1, 4] |
QUICKSORT |
False |
0 |
8 |
1 |
2 |
7 |
4 |
|
|
INC LEFT |
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
9 |
|
|
|
|
DEC RIGHT |
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
4 |
|
[8, 2, 6, 1, 7, 4, 1, 9] |
SWAP |
|
|
|
5 |
4 |
7 |
9 |
|
|
INC LEFT |
|
|
|
6 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
9 |
|
|
|
|
DEC RIGHT |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
1 |
|
[1, 2, 6, 1, 7, 4, 8, 9] |
SWAP PIVOT |
True |
6 |
8 |
7 |
9 |
0 |
1 |
|
[1, 2, 6, 1, 7, 4] |
QUICKSORT |
False |
0 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
5 |
4 |
|
|
INC LEFT |
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
DEC RIGHT |
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
4 |

Responses