Computer-Science-A-level-Ocr
-
3-3-networks8 主题
-
3-2-databases7 主题
-
3-1-compression-encryption-and-hashing4 主题
-
2-5-object-oriented-languages7 主题
-
2-4-types-of-programming-language4 主题
-
2-3-software-development5 主题
-
2-2-applications-generation6 主题
-
2-1-systems-software8 主题
-
1-3-input-output-and-storage2 主题
-
1-2-types-of-processor3 主题
-
1-1-structure-and-function-of-the-processor1 主题
-
structuring-your-responses3 主题
-
the-exam-papers2 主题
-
8-2-algorithms-for-the-main-data-structures4 主题
-
8-1-algorithms10 主题
-
7-2-computational-methods11 主题
-
7-1-programming-techniques14 主题
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
entity-relationship-diagrams
-
data-normalisation
-
relational-databases
-
hashing
-
symmetric-vs-asymmetric-encryption
-
run-length-encoding-and-dictionary-coding
-
lossy-and-lossless-compression
-
polymorphism-oop
-
encapsulation-oop
-
inheritance-oop
-
attributes-oop
-
methods-oop
-
objects-oop
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
6-5-thinking-concurrently2 主题
-
6-4-thinking-logically2 主题
-
6-3-thinking-procedurally3 主题
-
6-2-thinking-ahead1 主题
-
6-1-thinking-abstractly3 主题
-
5-2-moral-and-ethical-issues9 主题
-
5-1-computing-related-legislation4 主题
-
4-3-boolean-algebra5 主题
-
4-2-data-structures10 主题
-
4-1-data-types9 主题
-
3-4-web-technologies16 主题
-
environmental-effects
-
automated-decision-making
-
computers-in-the-workforce
-
layout-colour-paradigms-and-character-sets
-
piracy-and-offensive-communications
-
analysing-personal-information
-
monitoring-behaviour
-
censorship-and-the-internet
-
artificial-intelligence
-
the-regulation-of-investigatory-powers-act-2000
-
the-copyright-design-and-patents-act-1988
-
the-computer-misuse-act-1990
-
the-data-protection-act-1998
-
adder-circuits
-
flip-flop-circuits
-
simplifying-boolean-algebra
-
environmental-effects
dijkstras-shortest-path-algorithm
Dijkstra’s Shortest Path Algorithm
What is Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm?
-
In A Level Computer Science, Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm is an example of an optimisation algorithm that calculates the shortest path from a starting location to all other locations
-
Dijkstra’s uses a weighted graph in a similar manner to a breadth first search to exhaust all possible routes to find the optimal route to the destination node
-
To revise Graphs you can follow this link
-
Each route is represented as an arc/edge from a node/vertex. Each edge carries a weighted value which represents some measurement, for example time, distance or cost
-
An illustrated example of Dijkstra’s is shown below
What is an optimisation problem?
-
Optimisation problems involve maximising the efficiency of a solution to solve the stated problem. Examples of optimisation problems can include:
-
Finding the shortest route between two points. This is used for planning journeys, creating networks, building circuit boards, etc.
-
Minimising resource usage in manufacturing or games
-
Timetabling lessons in school or office meetings
-
Scheduling staff breaks and work hours
-
-
The most common optimisation problem encountered in daily life is finding the shortest route from A to B. Various apps exist to calculate these distances, such as Google Maps or road trip planners
Performing Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm
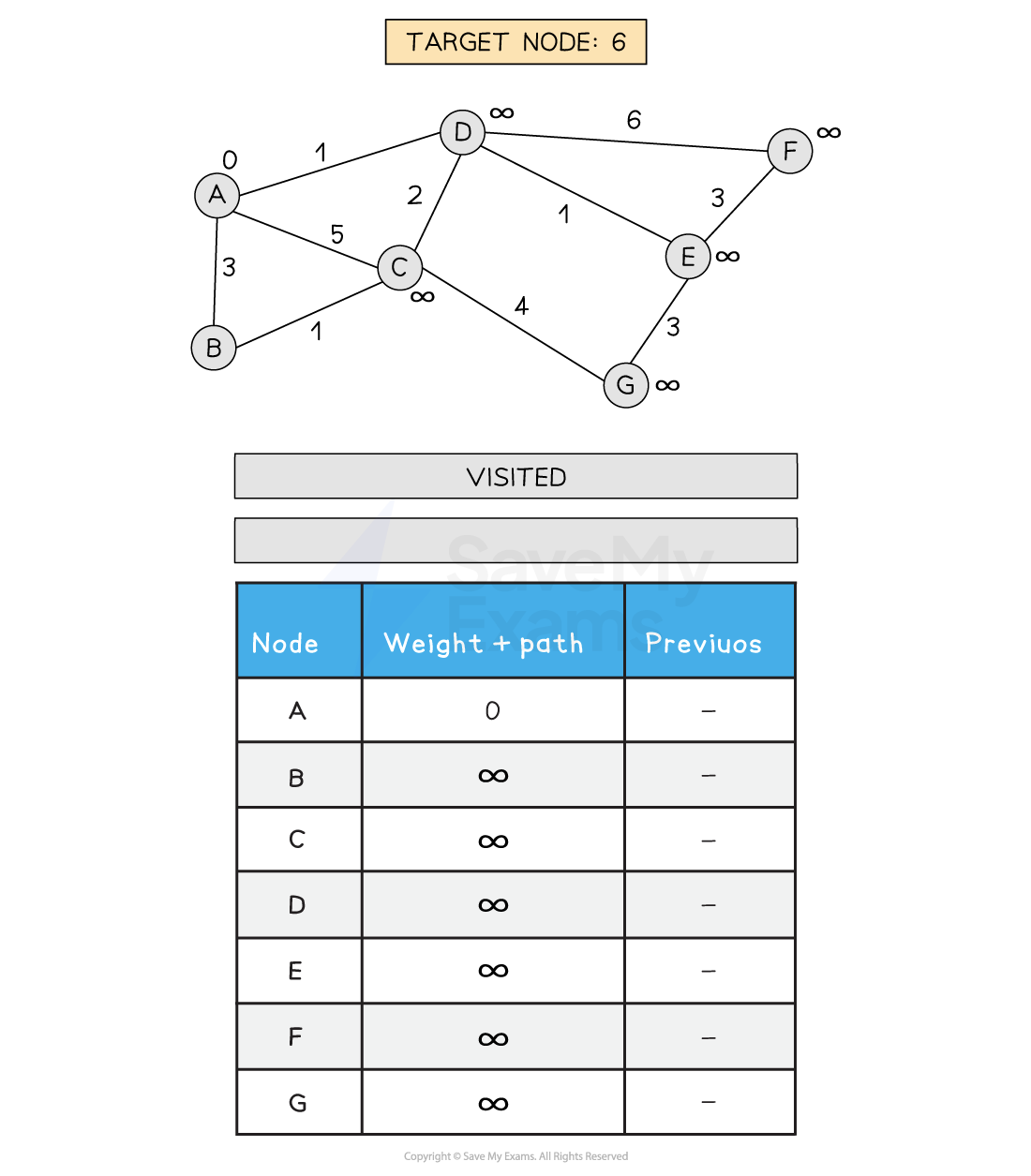
1) Set A path to 0 and all other path weights to infinity
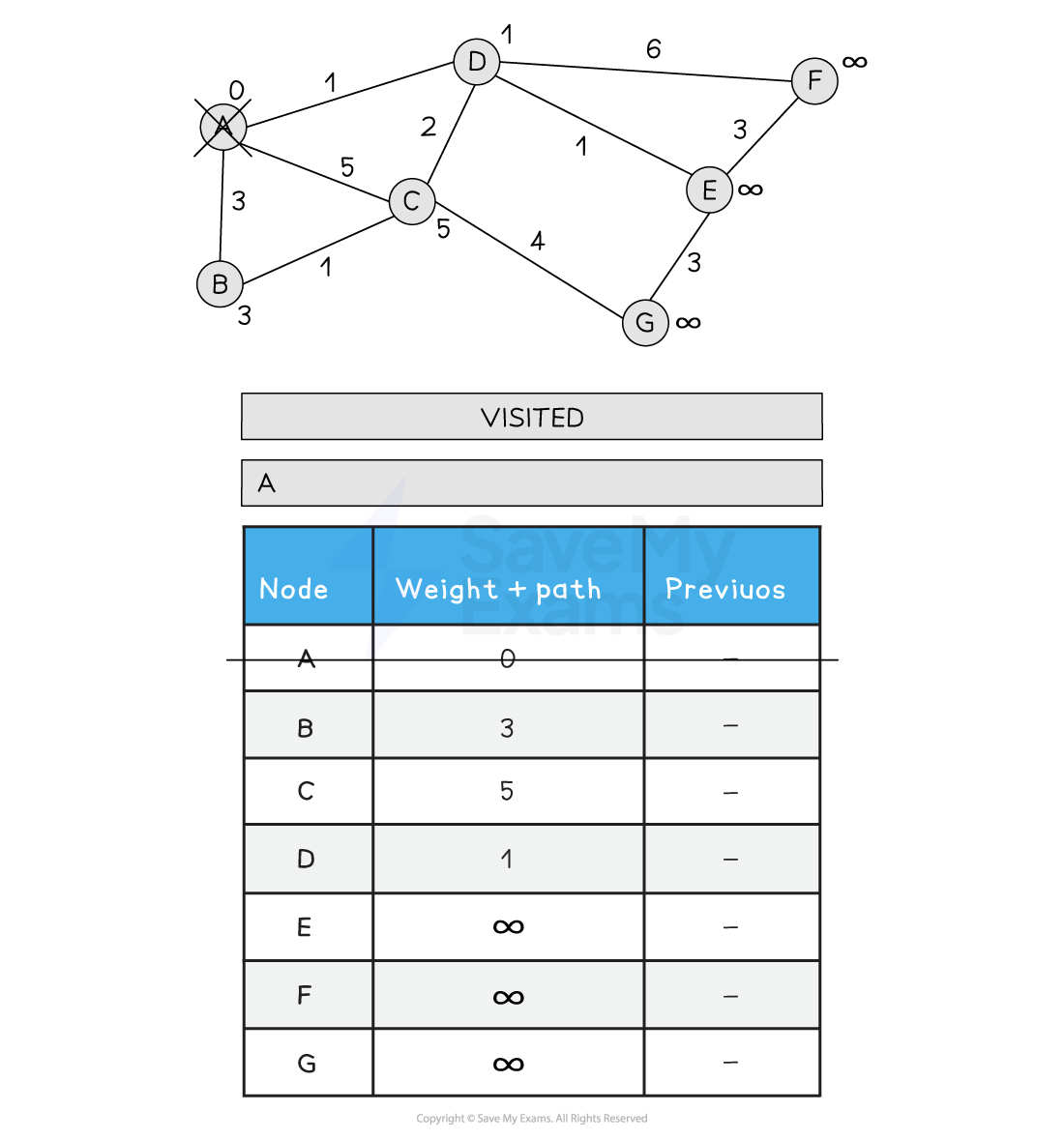
2) Visit A. Update all neighbouring nodes path weights to the distance from A + A’s path weight (0)
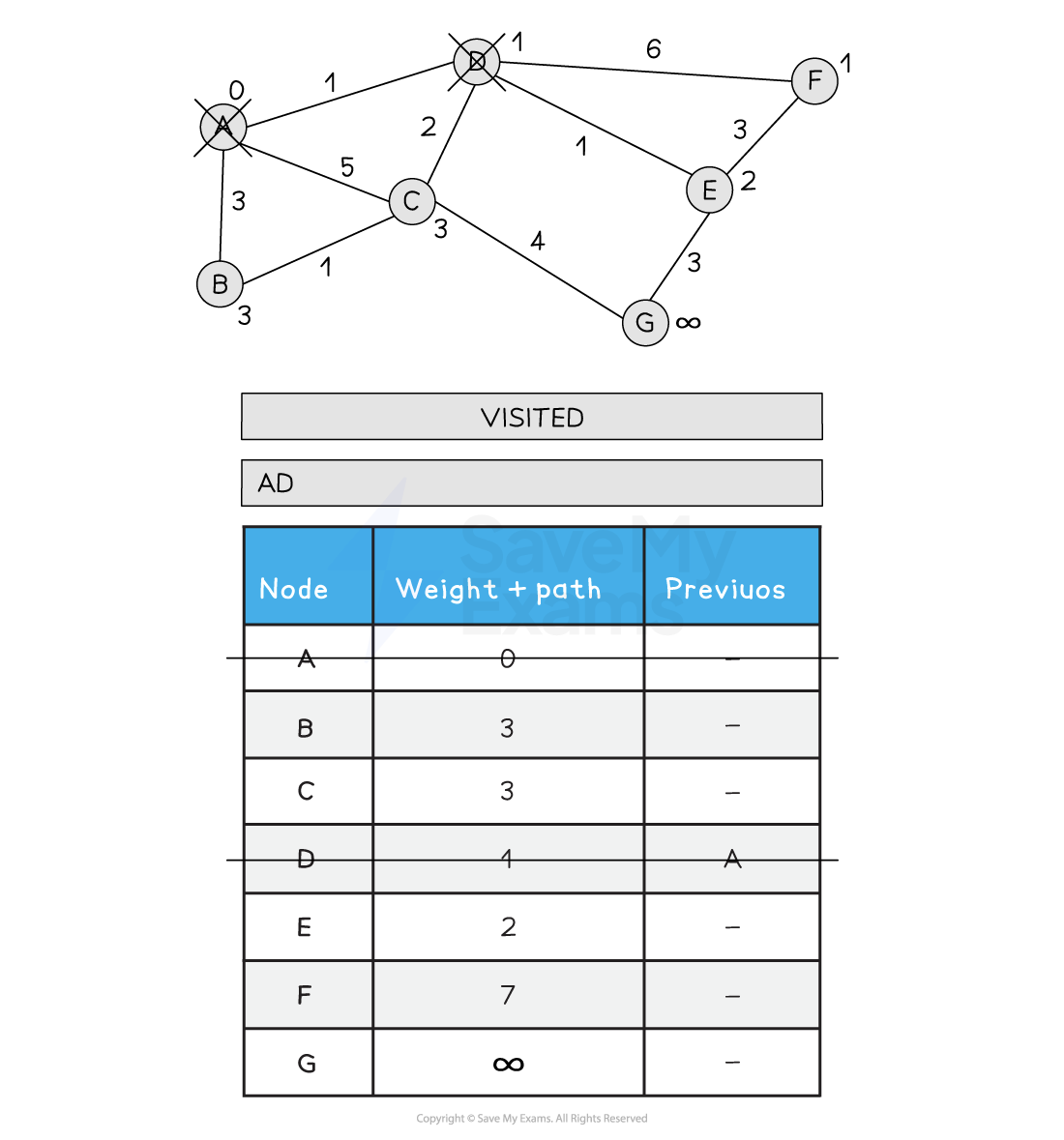
3) Choose the next node to visit that has the lowest path weight (D). Visit D. Update all neighbouring, non-visited nodes with a new path weight if the old path weight is bigger than the new path weight. C is updated from 5 to 3 as the new path is shorted (A > D > C)
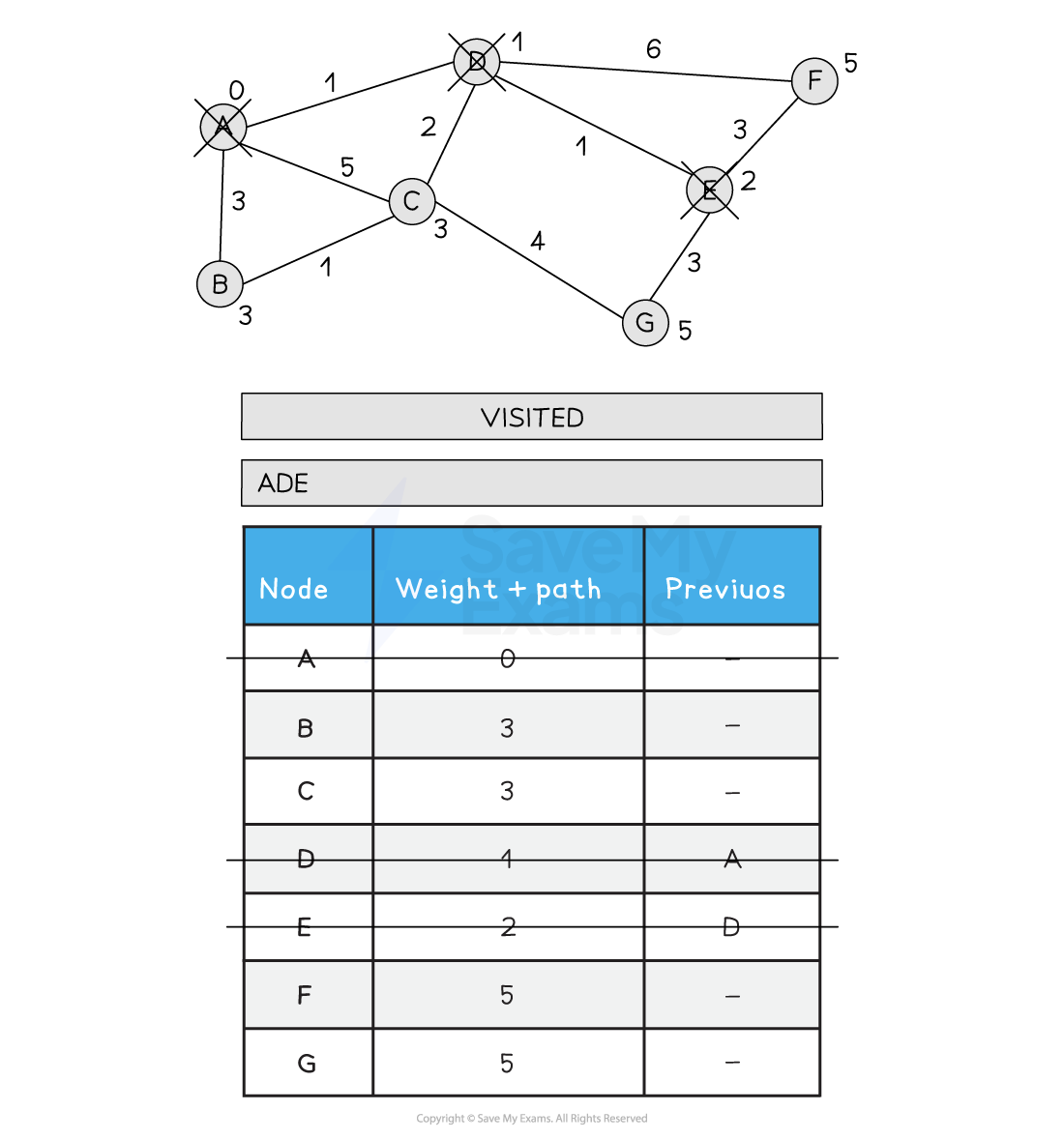
4) Choose the next node to visit that has the lowest path weight (E). Visit E. Update all neighbouring, non-visited nodes from E with a new path weight. F is updated from 7 to 5 as the new path is shorter (A > D > E > F)
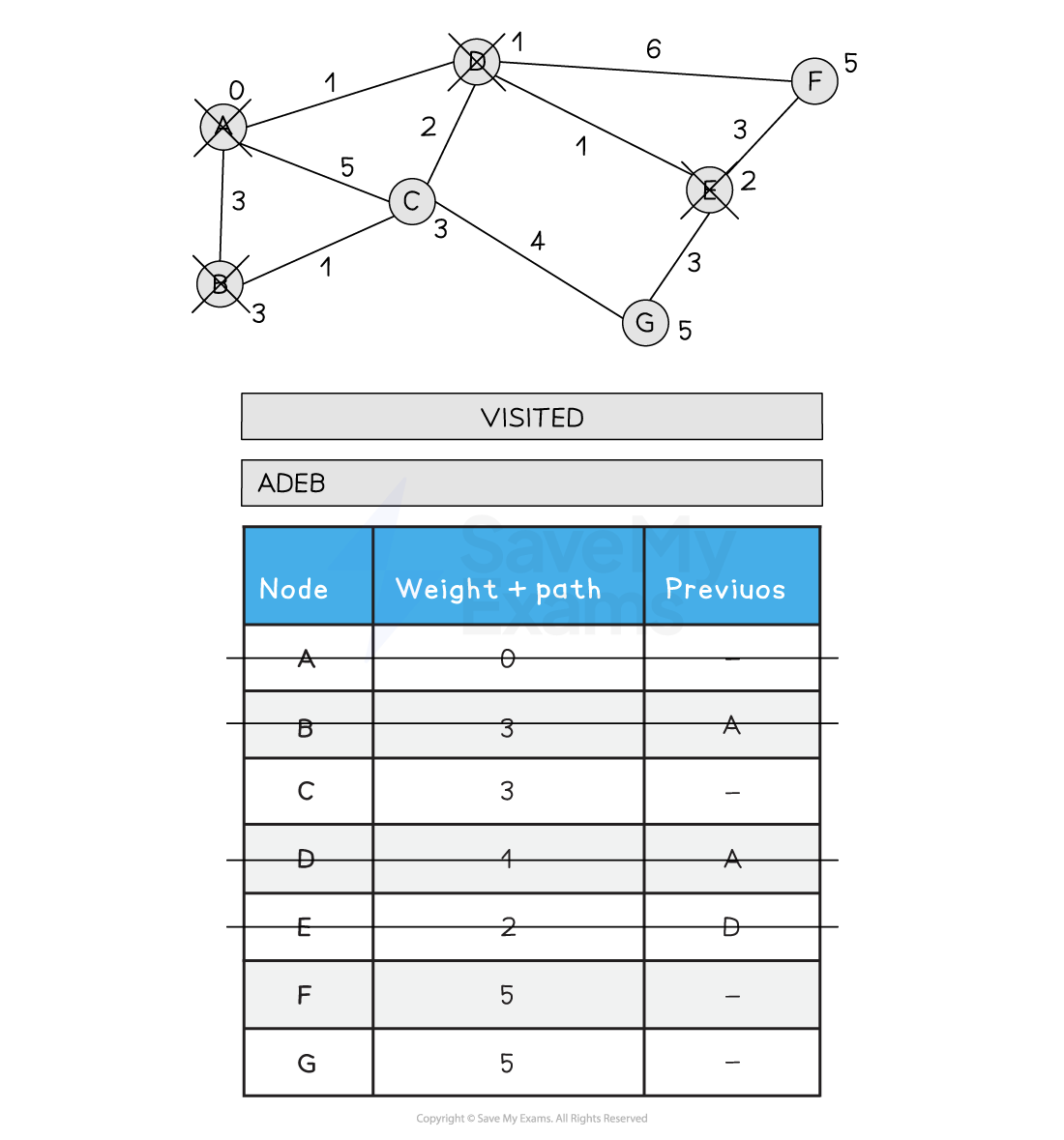
5) Choose the next node to visit, alphabetically (B). Visit B. Update all neighbouring non-visited nodes from B with a new weight if the path is less than the current path. C is not updated as A > B > C is 4
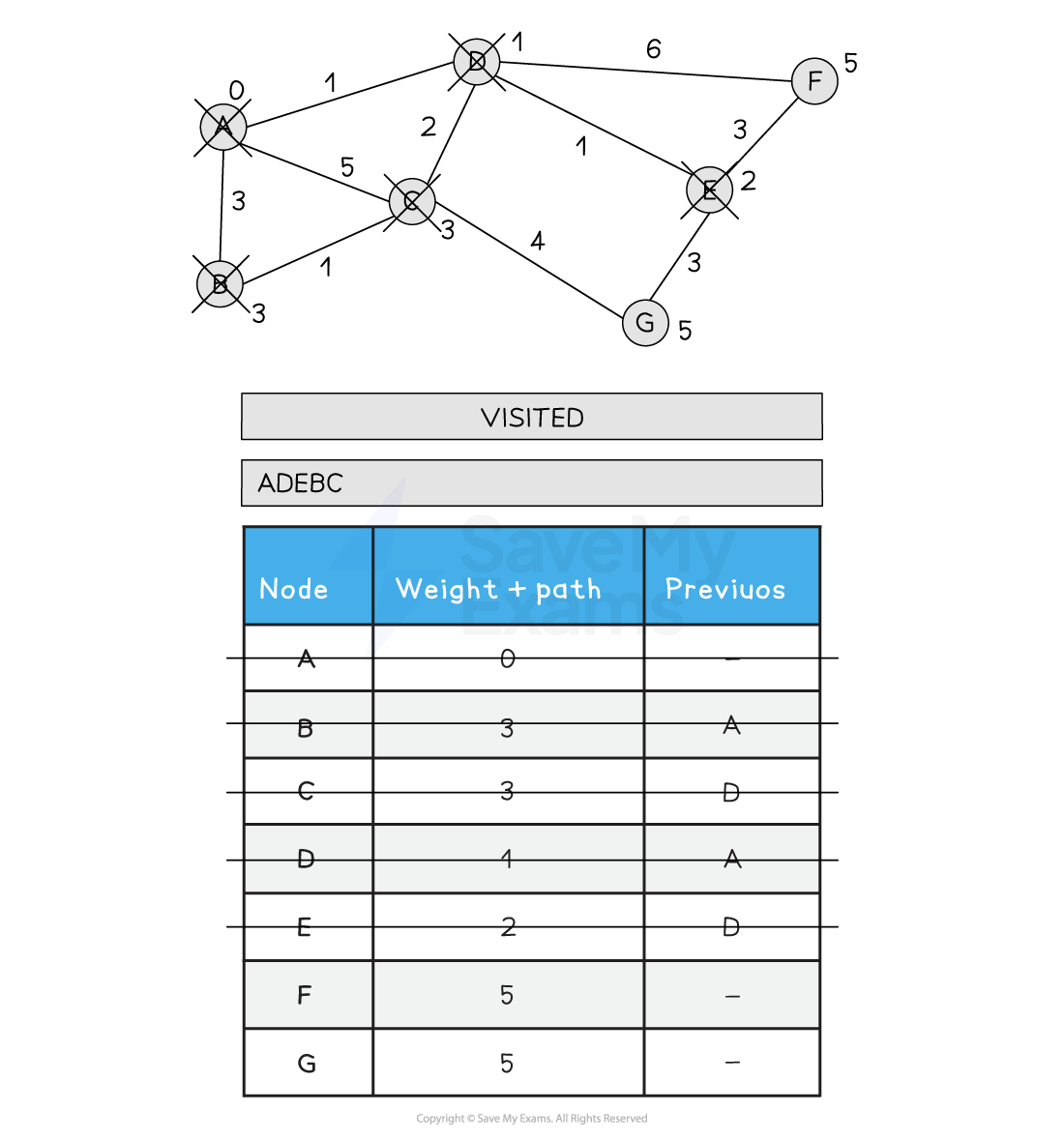
6) Choose the next lowest node and visit (C). Update C’s neighbours if the new path is shorter than the old path. A > D > C > G is 8, so G is not updated
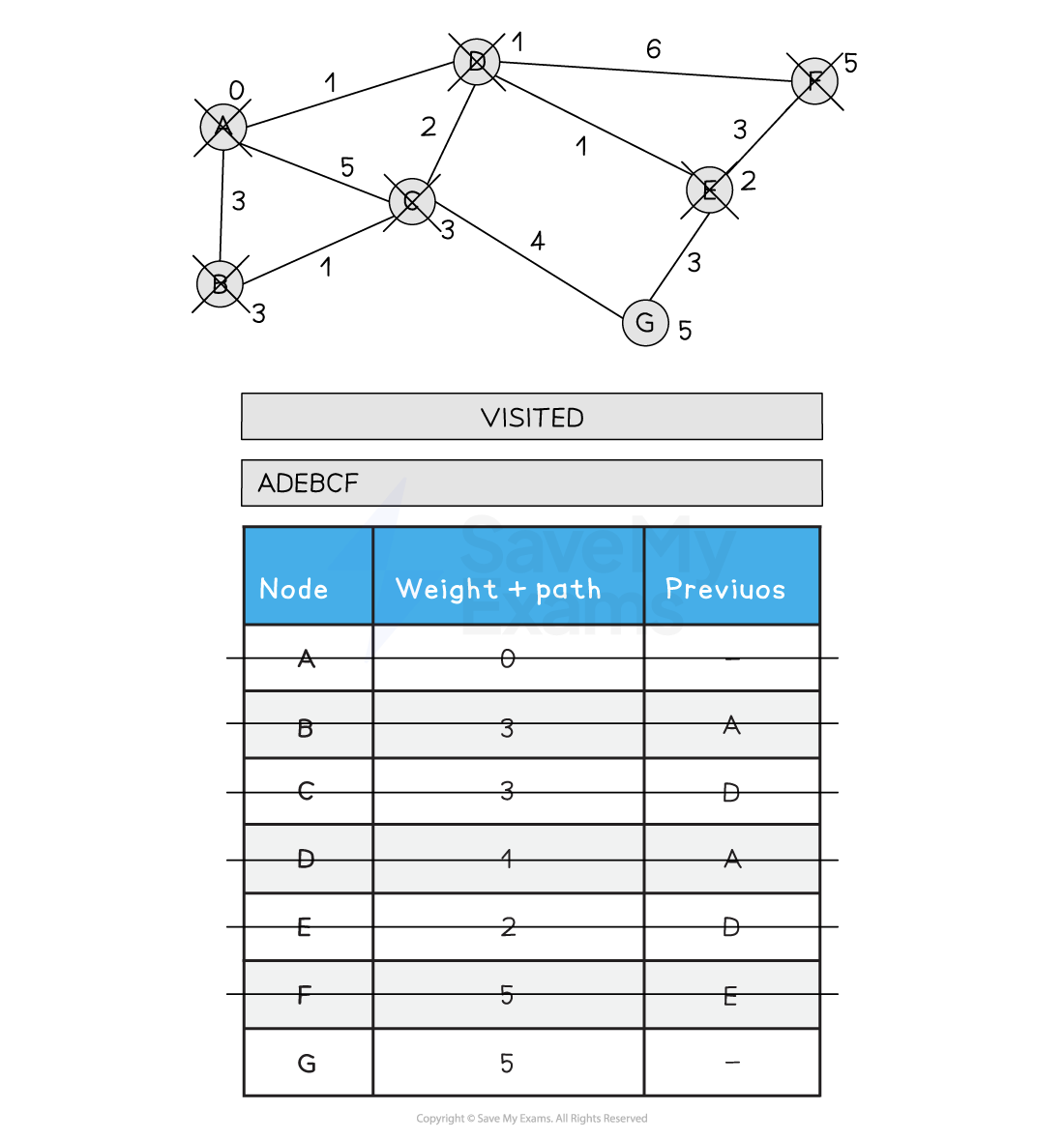
7) Choose the next lowest node and visit (F). Update F’s neighbours if the new path is shorter than the old path. F has no non-visited neighbours so no updates are made
<div class=”mb-5″

Responses