Computer-science_A-level_Cie
-
computers-and-components6 主题
-
logic-gates-and-logic-circuits2 主题
-
central-processing-unit-cpu-architecture6 主题
-
assembly-language-4 主题
-
bit-manipulation1 主题
-
operating-systems3 主题
-
language-translators2 主题
-
data-security3 主题
-
data-integrity1 主题
-
ethics-and-ownership3 主题
-
database-concepts3 主题
-
database-management-systems-dbms-1 主题
-
data-definition-language-ddl-and-data-manipulation-language-dml1 主题
-
computational-thinking-skills1 主题
-
algorithms14 主题
-
data-types-and-records2 主题
-
arrays2 主题
-
files1 主题
-
introduction-to-abstract-data-types-adt1 主题
-
programming-basics1 主题
-
constructs2 主题
-
structured-programming1 主题
-
program-development-life-cycle2 主题
-
program-design-2 主题
-
program-testing-and-maintenance3 主题
-
user-defined-data-types1 主题
-
file-organisation-and-access-3 主题
-
floating-point-numbers-representation-and-manipulation3 主题
-
protocols2 主题
-
circuit-switching-packet-switching1 主题
-
processors-parallel-processing-and-virtual-machines5 主题
-
boolean-algebra-and-logic-circuits4 主题
-
purposes-of-an-operating-system-os3 主题
-
translation-software3 主题
-
encryption-encryption-protocols-and-digital-certificates3 主题
-
artificial-intelligence-ai4 主题
-
recursion1 主题
-
programming-paradigms4 主题
-
object-oriented-programming7 主题
-
file-processing-and-exception-handling2 主题
-
data-representation5 主题
-
multimedia3 主题
-
compression2 主题
-
networks-and-the-internet11 主题
binary-trees
Binary trees
What is a binary tree?
-
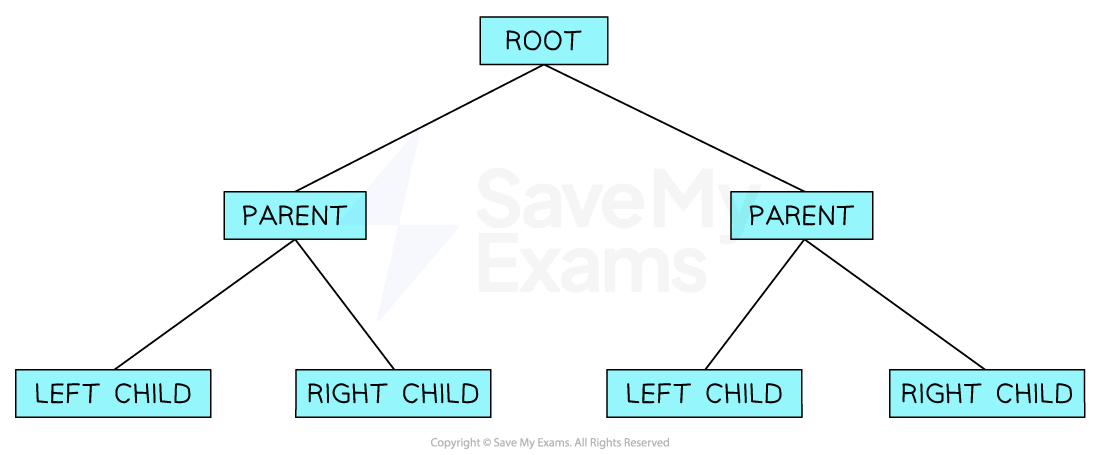
A binary tree is a rooted tree where every node has a maximum of 2 nodes
-
A binary tree is essentially a graph and therefore can be implemented in the same way
-
You must understand:
-
Tree traversal of a tree data structure
-
Add new data to a tree
-
Remove data from a tree
-
-
The most common way to represent a binary tree is by storing each node with a left and right pointer
This information is usually implemented using 2D arrays

Tree terminology
|
Keyword |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Node |
An item in a tree |
|
Edge |
Connects two nodes together and is also known as a branch or pointer |
|
Root |
A single node which does not have any incoming nodes |
|
Child |
A node with incoming edges |
|
Parent |
A node with outgoing edges |
|
Subtree |
A subsection of a tree consisting of a parent and all the children of a parent |
|
Leaf |
A node with no children |
|
Traversing |
The process of visiting each node in a tree data structure, exactly once |
How do you program a tree?
-
In the following example:
-
A tree is represented using a
TreeNodestructure, which includes:-
A
valuefield to store the data held in the node -
A
childrenfield to store a collection (e.g. list or array) of child nodes
-
-
The
createTreeNodefunction is used to initialise a new tree node, setting its value and creating an empty collection for its children -
The
addChildfunction allows a new child node to be added to a parent node-
It creates a new
TreeNodewith the given value and appends it to the parent’schildrencollection
-
-
Finally, the
createTreeNodefunction is used to create the root node-
Additional child nodes are added using the
addChildfunction, allowing a multi-level tree structure to be built with branches and sub-branches
-
-
|
Pseudocode |
|---|
|
|
Python |
|---|
|
|
Java |
|---|
|
Algorithm to traverse a tree structure
|
Pseudocode – pre-order tree traversal |
|---|
|
|
Python – pre-order tree traversal |
|---|
|
|
Java – pre-order tree traversal |
|---|
|
-
For a tree like:
Root├── Child 1│ └── Grandchild 1.1└── Child 2 -
The output will be:
RootChild 1Grandchild 1.1Child 2
Algorithm to add data to a tree structure
|
Pseudocode |
|---|
|
|
Python |
|---|
|
|
Java |
|---|
|
-
These examples all create a new node with the provided value and attach it to the given parent node
-
This approach allows dynamic construction of trees with multiple levels
Algorithm to remove data to a tree structure
|
Pseudocode |
|---|
|
|
Python |
|---|
|
|
Java |
|---|
|
-
This only removes the first matching child from the direct children of a node
-
If you want to remove nodes anywhere in the tree, you’d need a recursive version
-
REMOVEanddeland.remove()work because thechildrencollection is a list/array

Responses