Computer-science_A-level_Cie
-
computers-and-components6 主题
-
logic-gates-and-logic-circuits2 主题
-
central-processing-unit-cpu-architecture6 主题
-
assembly-language-4 主题
-
bit-manipulation1 主题
-
operating-systems3 主题
-
language-translators2 主题
-
data-security3 主题
-
data-integrity1 主题
-
ethics-and-ownership3 主题
-
database-concepts3 主题
-
database-management-systems-dbms-1 主题
-
data-definition-language-ddl-and-data-manipulation-language-dml1 主题
-
computational-thinking-skills1 主题
-
algorithms14 主题
-
data-types-and-records2 主题
-
arrays2 主题
-
files1 主题
-
introduction-to-abstract-data-types-adt1 主题
-
programming-basics1 主题
-
constructs2 主题
-
structured-programming1 主题
-
program-development-life-cycle2 主题
-
program-design-2 主题
-
program-testing-and-maintenance3 主题
-
user-defined-data-types1 主题
-
file-organisation-and-access-3 主题
-
floating-point-numbers-representation-and-manipulation3 主题
-
protocols2 主题
-
circuit-switching-packet-switching1 主题
-
processors-parallel-processing-and-virtual-machines5 主题
-
boolean-algebra-and-logic-circuits4 主题
-
purposes-of-an-operating-system-os3 主题
-
translation-software3 主题
-
encryption-encryption-protocols-and-digital-certificates3 主题
-
artificial-intelligence-ai4 主题
-
recursion1 主题
-
programming-paradigms4 主题
-
object-oriented-programming7 主题
-
file-processing-and-exception-handling2 主题
-
data-representation5 主题
-
multimedia3 主题
-
compression2 主题
-
networks-and-the-internet11 主题
computer-architectures
Architecture types
What is a computer architecture?
-
A computer architecture is the design and structure of a computer system
-
It describes how it fetches, processes, and stores data and instructions
-
It defines how components like the CPU, memory, and input/output devices work together to execute programs
-
Each architecture is categorised as:
-
Single or Multiple Instruction stream
-
Single or Multiple Data stream
-
SISD – Single Instruction, Single Data
|
Description |
Key Features |
|---|---|
|
One processor executes one instruction on one data stream at a time |
Traditional serial (non-parallel) architecture |
|
Used in basic, single-core processors |
Step-by-step processing |
Example: Classic desktop CPU running one task at a time

SIMD – Single Instruction, Multiple Data
|
Description |
Key Features |
|---|---|
|
One instruction is applied to multiple pieces of data at once |
Useful for parallel processing |
|
All processing units perform the same operation in parallel |
Ideal for graphics or scientific computation |
Example: GPU operations, image processing

MISD – Multiple Instruction, Single Data
|
Description |
Key Features |
|---|---|
|
Multiple processors execute different instructions on the same data |
Very uncommon in practice |
|
Used in specialised systems for fault tolerance |
Each unit checks the same input differently |
Example: Redundant systems in safety-critical environments
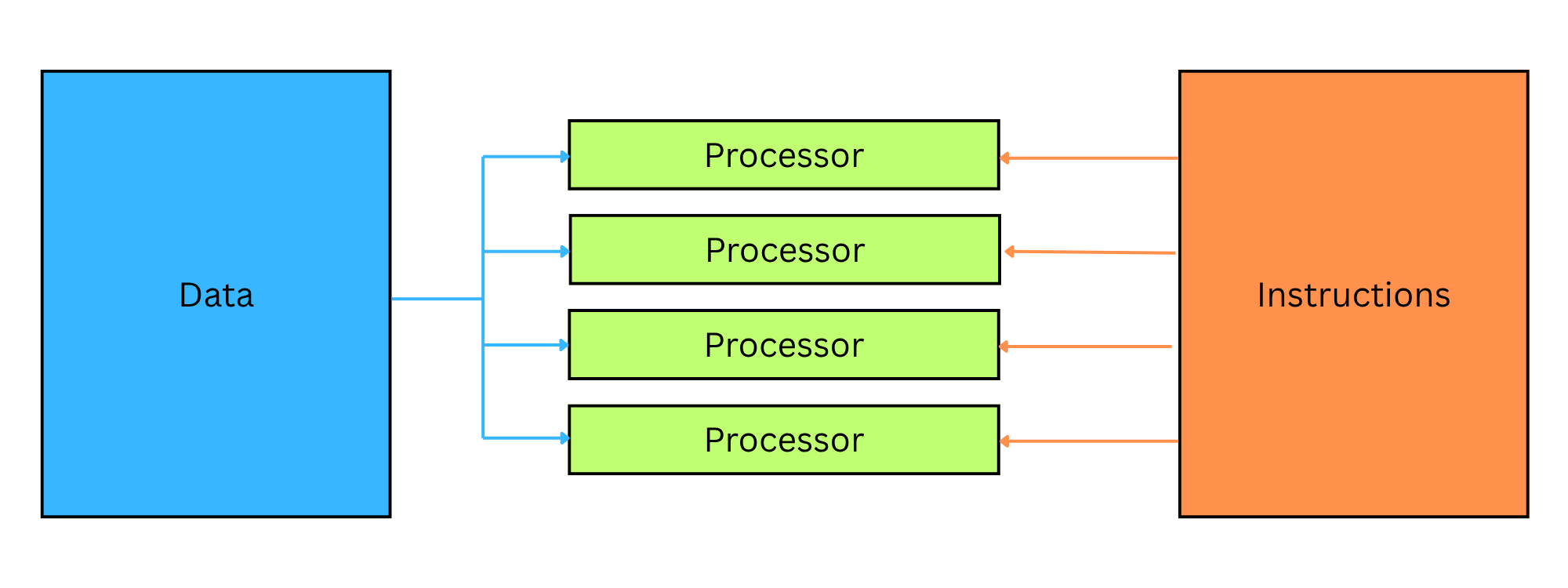
MIMD – Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data
|
Description |
Key Features |
|---|---|
|
Multiple processors execute different instructions on different data sets |
Most modern multi-core processors use this model |
|
Allows full concurrent processing of independent tasks |
Flexible and scalable for parallel programs |
Example: Multi-core CPUs, distributed systems, cloud computing

Summary table
|
Architecture |
Instruction Stream |
Data Stream |
Used In |
|---|---|---|---|
|
SISD |
Single |
Single |
Standard sequential processors |
|
SIMD |
Single |
Multiple |
Vector processing (e.g. GPUs) |
|
MISD |
Multiple |
Single |
Specialised fault-tolerant systems |
|
MIMD |
Multiple |
Multiple |
Multi-core processors, parallel systems |

Responses