Development of corporate strategy
-
A successful corporate strategy helps to provide a competitive advantage
-
Effective corporate strategy development requires careful consideration of a range of internal factors and the external environment in which the business operates
-
Internal factors include the human and capital resources available
-
External factors include the economic and political environments
-
-
Two strategic models used to develop a corporate strategy are the Ansoff matrix and Porter’s strategic matrix
The Ansoff matrix
-
The Ansoff matrix is a tool for businesses with a growth objective
-
It is used to identify an appropriate corporate strategy and the level of risk associated with the chosen strategy
-
The model considers four elements, which are broken down into two categories:
-
The market — existing and new markets
-
The product — existing and new products
-
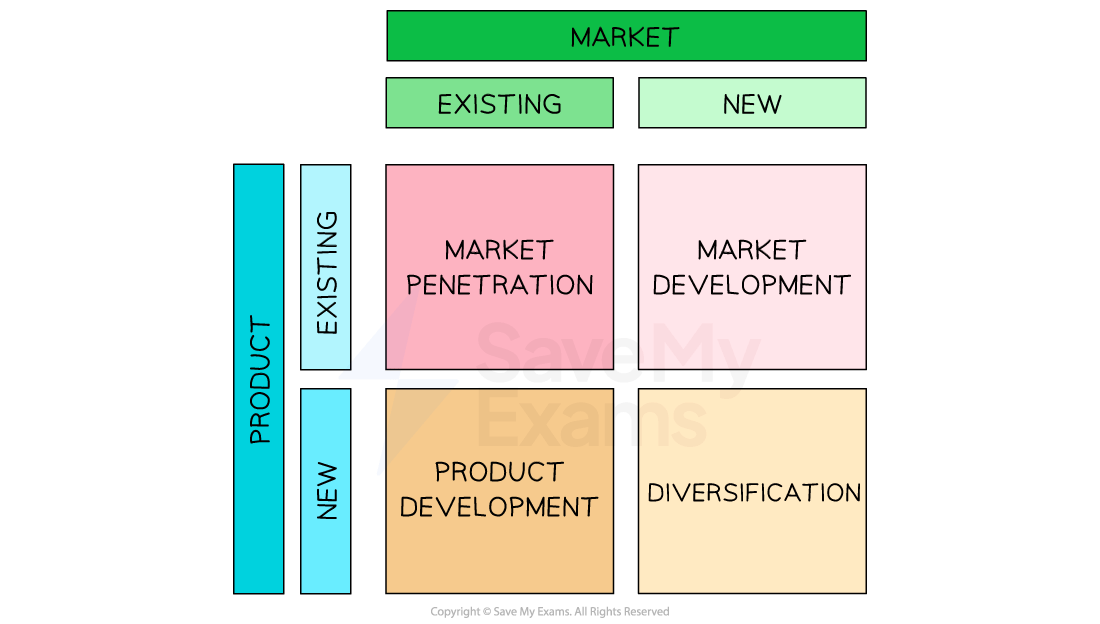
The Ansoff matrix: strategies for growth
-
The least risky strategy to achieve growth is to pursue a strategy of market penetration
-
This involves selling more products to existing customers by encouraging:
-
More regular use of the product
-
Increased use of the product
-
Brand loyalty of customers
-
-
-
Market development involves finding and exploiting new market opportunities for existing products by:
-
Entering new markets at home or abroad
-
Repositioning the product by selling to different customer profiles (selling to other businesses as well as directly to consumers)
-
Seeking complementary locations
-
For example, M&S Food has achieved significant growth since teaming up with fuel retailers such as BP and Applegreen and providing express retail outlets
-
-
-
Product development involves selling new or improved products to existing customers by:
-
Developing new versions or upgrades of existing successful products
-
Redesigning packaging and aesthetic features
-
Relaunching heritage products at commercially convenient intervals
-
For example, Cadbury relaunches Christmas-themed products each year, often with a subtle design change, to recapture the interest of customers
-
-
-
Diversification is the most risky growth strategy, as it involves targeting new customers with entirely new or redeveloped products
-
Examples of diversification include:
-
Tesco launching a range of financial products, including current accounts and credit cards
-
Greggs launching a range of themed clothing products
-
-
Porter’s generic strategic matrix
-
Porter’s generic strategic matrix identifies a range of strategies a business might adopt, considering:
-
Its source of competitive advantage (cost or differentiation)
-
The scope of the market in which it operates (mass or niche)
-
-
Porter argues that failing to adopt one of these strategies risks a business being “stuck in the middle” and unable to compete successfully with rivals in the market
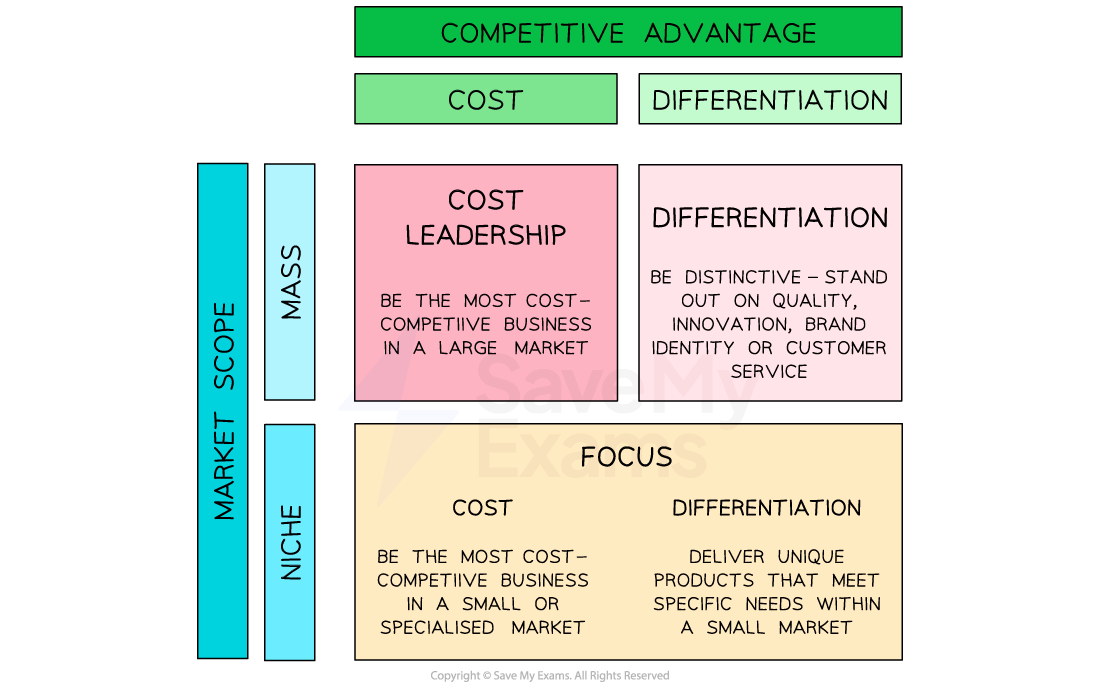
Porter’s generic matrix
-
Businesses operating in the mass market should adopt either a cost leadership or a differentiation strategy, depending on what it is that makes them stand out from their competitors
-
Businesses that have a significant cost advantage over competitors should exploit this as much as possible to achieve success, which is called cost leadership
-
Businesses that are unable to operate as the most competitive on cost should adopt a strategy of differentiation
-
-
A business that operates in a niche market should adopt a focus strategy that closely meets the needs of its specific group of customers
-
A cost focus involves being the lowest cost competitor within the market niche
-
A differentiation focus involves offering specialised products within the niche market
-
Portfolio analysis
-
Portfolio analysis involves a business carrying out a detailed evaluation of its full range of products so that appropriate strategies may be identified and pursued
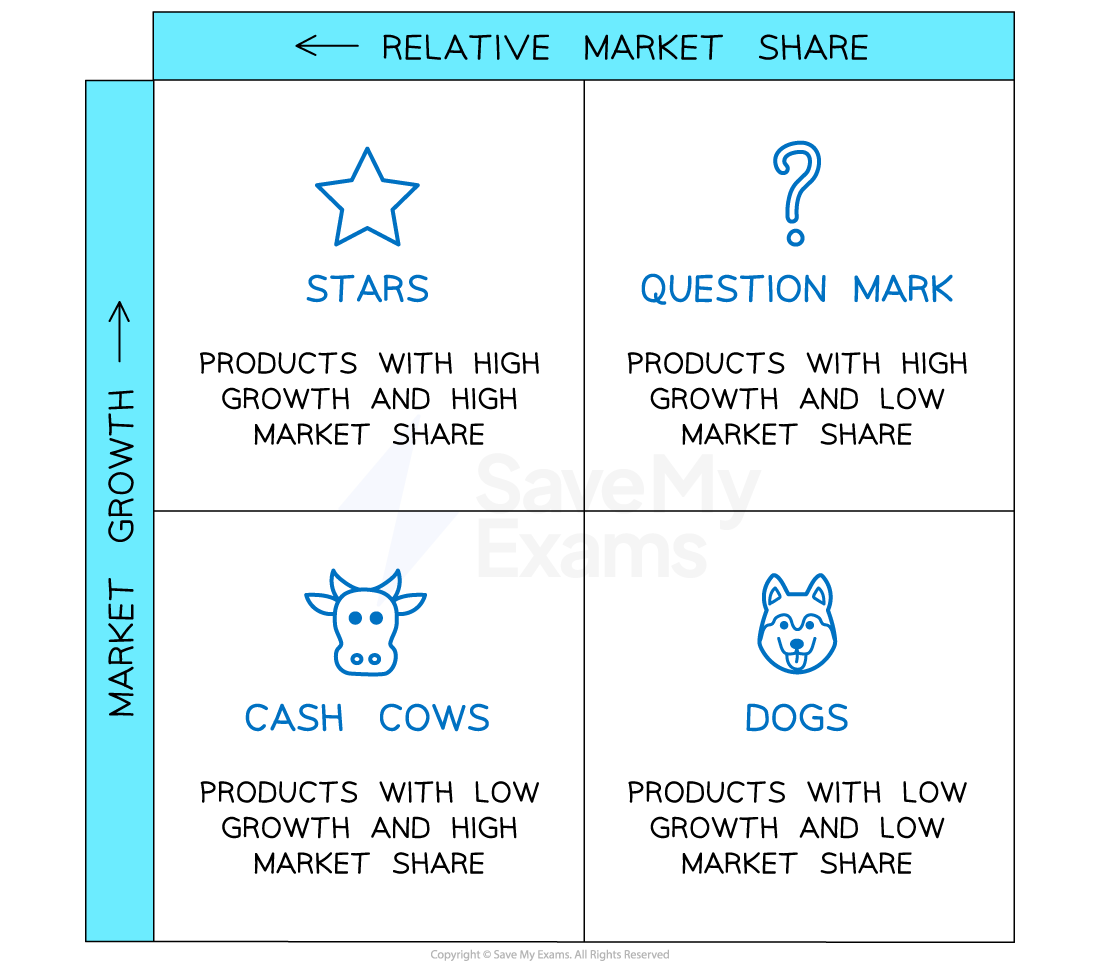
Boston matrix
-
The Boston Matrix is a portfolio analysis tool that considers the relative market share of a firm’s products and the rate of growth within the market in which each product is sold
-
Stars are products sold in high-growth markets and have a high level of market share
-
Stars require some ongoing investment to maintain their market position and, if managed well, they are likely to become cash cows in the future
-
A market penetration strategy to increase sales revenue and maximise market share is likely to be appropriate
-
-
Cash cows are sold in lower-growth markets and have a high market share
-
Cash cows generate more cash than they need to maintain their market position and can be used to fund the development of other products in the portfolio
-
Businesses may seek new markets for these products if they are relatively risk-free
-
-
Question marks are sold in high-growth markets and have a relatively low market share
-
Question marks require significant investment if they are to improve their level of market share and become stars
-
There is a risk that question marks will become dogs when market growth rates slow
-
-
Dogs are sold in low-growth markets and have a relatively low market share
-
Dogs have little potential for future growth and should be divested so that finance and effort may be invested in other products
-
Achieving competitive advantage through distinctive capabilities
-
When a business has a particular strength that is very difficult for competitors to copy, it has a distinctive capability
-
The nature of that distinctive capability will determine the aims and objectives of the business and the strategies it will pursue to achieve them
Examples of distinctive capabilities
|
Distinctive capability |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Responses