Market positioning and market mapping
-
Market positioning refers to the process a business goes through when launching a new product or service
-
The business decides where it wants to position its product in the market with regard to price, quality, branding and customer perception
-
-
Market mapping is a tool for identifying the position of a product within a market
-
A market map refers to a two-dimensional diagram that shows the attributes or characteristics of a product in comparison to rivals’ products
-
Only two criteria can be chosen: price and quality, age and income, etc.
-
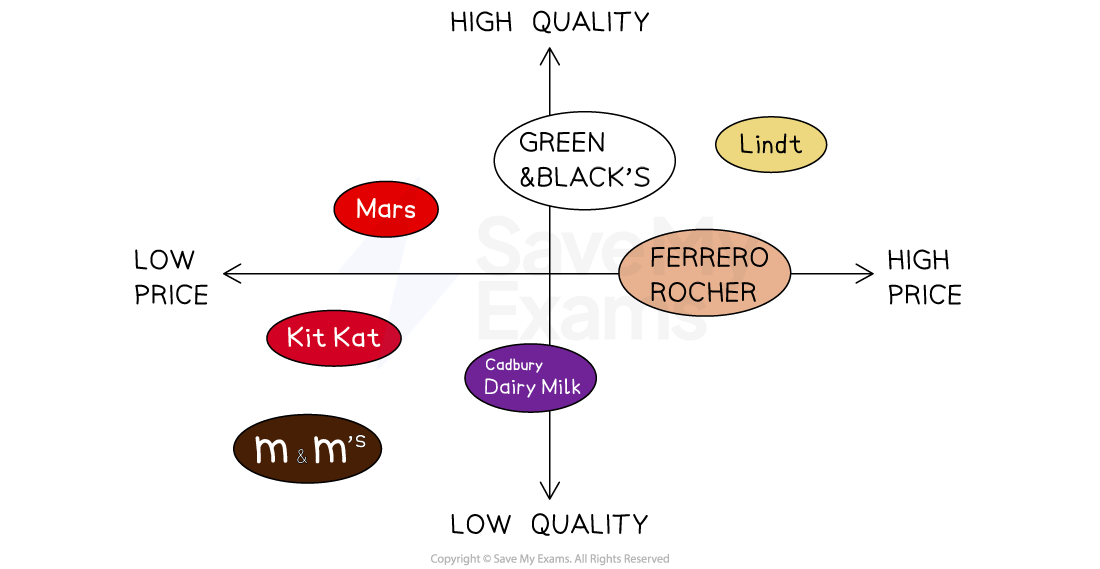
Market map analysis
-
If there were no spaces left on the market map, it indicates that the market is saturated
-
This means that there are no opportunities to exploit a market niche in the market
-
Competition is likely to be high and profits low
-
-
However, the existence of a space on the market map may indicate the existence of a market niche
-
This needs to be researched carefully before the business commits. E.g. it looks like there is a gap in the market in the high price / low quality area in the map above
-
However, this gap does not represent a worthwhile market, as the business would find it impossible to build and maintain a loyal customer base
-
The usefulness and limitations of market mapping
|
Usefulness |
Limitations |
|---|---|
|
|
Competitive advantage of a product or service
-
Competitive advantage refers to the features of a business and its products that are perceived as superior to its rivals by customers
-
It is how a firm’s product is made both distinctive and defensible
-
Distinctive means that the product is different from those of competitors
-
Defensible means that the business can prevent competitors from copying the product
-
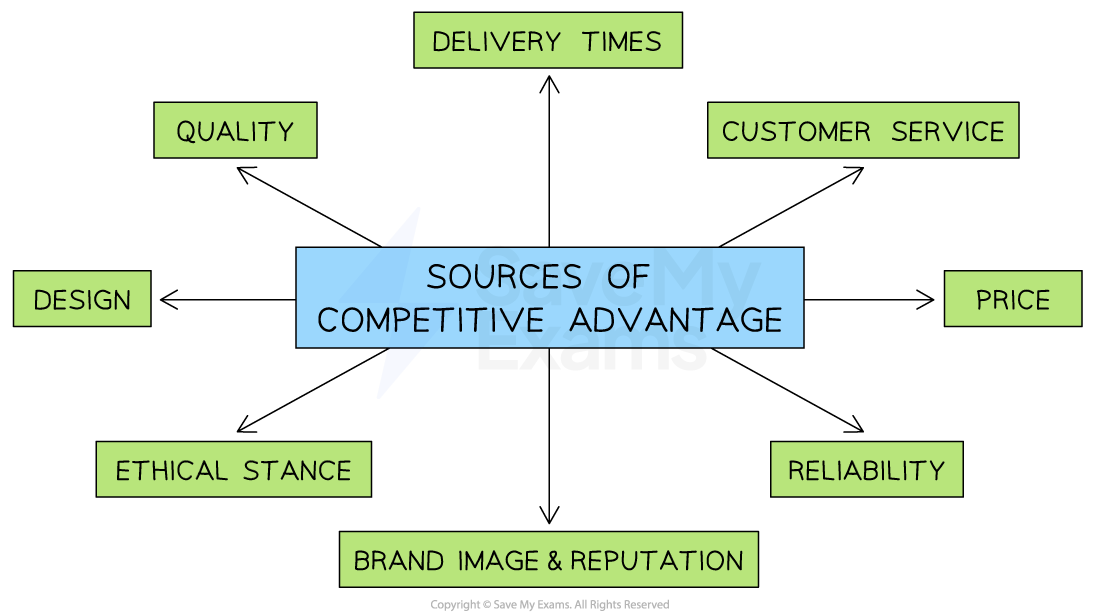
Source of competitive advantage
-
There are many ways a firm can gain a competitive advantage, including:
-
Innovation and reputation (branding)
-
Building strong relationships with stakeholders
-
Adding value
-
Differentiation
-
Market segmentation
-
Price leadership
-
-
Examples of the source of a business’s competitive advantage include:
-
Quality; e.g. Audi is well known for the exceptional quality of the finishing inside its cars
-
Delivery times; e.g. Amazon Prime delivers products within 24 hours of ordering
-
Low price; e.g. Primark is considered to provide the best value / low price combination
-
Reliability; e.g. Apple Macs have an excellent reputation for long life and reliability
-
Ethical stance; e.g. Tony’s Chocolonely only uses cocoa in its chocolate, which is 100% free of slave/child production
-
Design; e.g. Dyson vacuum cleaners stand out from the crowd with their original design
-
The purpose of product differentiation
-
Product differentiation is an attempt by a business to distinguish its products from those of competitors
-
This involves creating functions or features of the product (or firm) that help it to stand out from its competitors
-
Strong product differentiation helps the firm develop its competitive advantage
-
The development of product differentiation often helps a firm create a unique selling point for its product, which can be used in marketing
-
Product differentiation may be tangible (clearly visible), or it may be a perception that is created about the product in the consumer’s mind
-
-
Successful product differentiation helps the business to increase demand for its products, increase brand loyalty and allow the business to charge higher prices
-
Examples of successful product differentiation include:
-
In 2014, Hyundai in Singapore introduced a three-year warranty on all its new cars, when the industry standard was one year
-
Green & Black’s uses Fairtrade cocoa and sugar in the production of its chocolate
-
Adding value to products/services
-
Adding value is the difference between the price that is charged to the customer and the cost of inputs required to create the product or service
-
E.g. customers are prepared to pay more for potatoes when they are packaged as oven chips than they would be willing to pay for a bag of whole potatoes
-
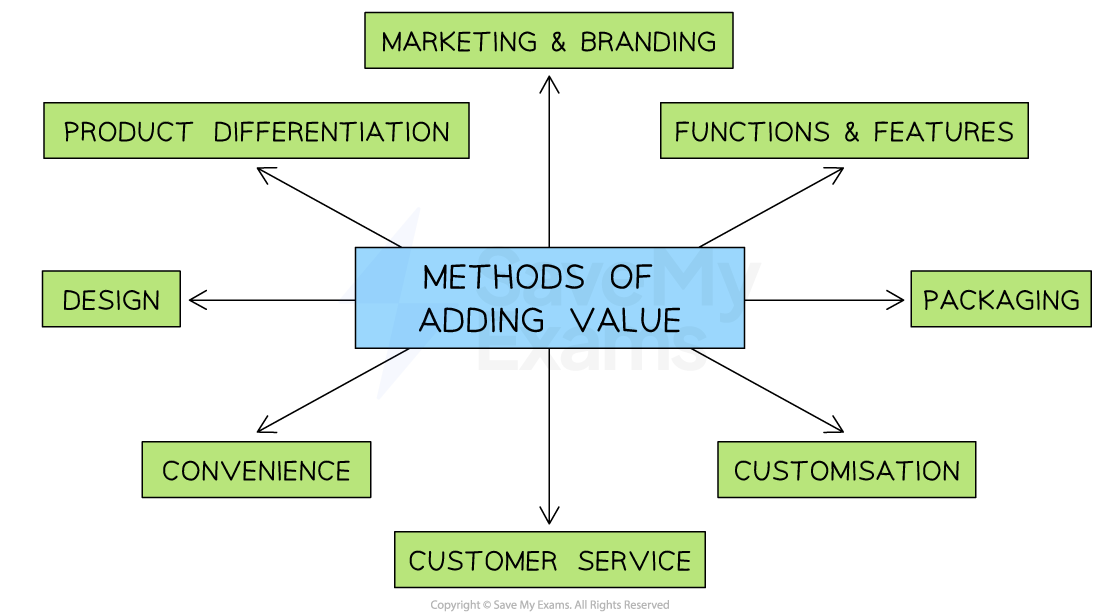
Methods of adding value
-
The methods of adding value overlap with some of the features of product differentiation:
-
Marketing and branding
Building brand identification and customer loyalty to the brand allows a firm to charge a higher price for its products, thus increasing the added value-
E.g. Yeezy 350 V2 sneakers sell for $250 a pair
-
-
Functions and features
Adding unique features allows a firm to charge a higher price for its products, thus increasing the added value-
E.g. The Samsung Galaxy Watch5 has robust health tracking tools built into it, along with an amazing screen
-
-
Customer service
Businesses that ensure they have a good reputation for customer service can charge a higher price for their products, thus increasing the added value-
E.g. John Lewis is considered to provide the best customer service amongst department stores in the UK
-
-
Customisation
Allowing customers to design or create their products allows a firm to charge a higher price, thus increasing the added value-
E.g. Moonpig birthday cards can be completely customised
-
-
Packaging
Apple products are well known for their superior packaging, which creates an exciting opening experience for the customer. This allows the firm to charge a higher price for its products, thus increasing the added value
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Businesses may use several methods of adding value.
Adding value often raises costs, but it is worth it if the increase in selling price outweighs the costs associated with the method.
For example, if improving the packaging costs £1 per unit and the firm can raise its selling price by £1,40 per unit, then profitability will improve.

Responses