Business_A-level_Cie
-
business-and-its-environment
enterprise6 主题 -
business-structure6 主题
-
size-of-business3 主题
-
business-objectives3 主题
-
stakeholders-in-a-business2 主题
-
external-influences-on-business12 主题
-
political-influences
-
legal-influences
-
economic-influences
-
economic-government-macroeconomic-objectives
-
economic-government-policies
-
social-influences
-
the-impact-of-corporate-social-responsibility
-
demographic-influences
-
technology-competitors-and-suppliers
-
international-trade
-
the-impact-of-multinationals
-
environmental-influences
-
political-influences
-
business-strategy10 主题
-
human-resource-managementhuman-resource-management-hrm8 主题
-
motivation4 主题
-
management2 主题
-
organisational-structure5 主题
-
business-communication5 主题
-
leadership2 主题
-
human-resource-strategy3 主题
-
marketingthe-nature-of-marketing7 主题
-
market-research3 主题
-
the-marketing-mix6 主题
-
marketing-analysis5 主题
-
marketing-strategy3 主题
-
operations-managementthe-nature-of-operations3 主题
-
inventory-management2 主题
-
capacity-utilisation-and-outsourcing1 主题
-
location-and-scale2 主题
-
quality-management1 主题
-
operations-strategy4 主题
-
finance-and-accountingbusiness-finance2 主题
-
sources-of-finance3 主题
-
forecasting-and-managing-cash-flows1 主题
-
costs4 主题
-
budgets1 主题
-
financial-statements4 主题
-
analysing-published-accounts6 主题
-
investment-appraisal2 主题
porters-five-forces-and-blue-ocean-strategy
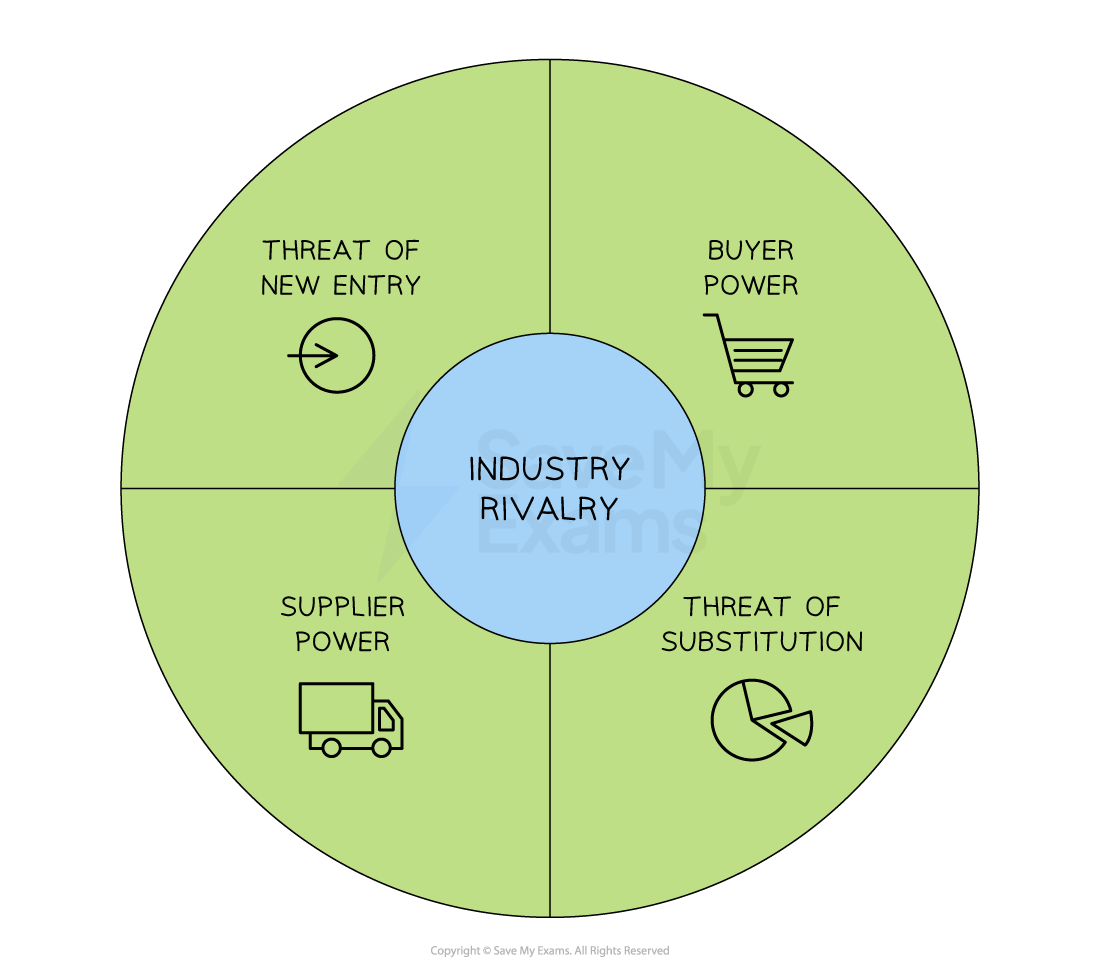
An introduction to Porter’s Five Forces model
-
Porter’s Five Forces identify the key pressures on an industry that impact the ability of a business to compete with rivals
-
It helps managers think strategically about the environment in which the business operates
-
Porter’s five forces
-
Once a business fully understands these pressures in their context, they can take strategic decisions to achieve and sustain a competitive advantage
Explanation of Porter’s five forces model
|
Force |
Explanation |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Industry rivalry |
|
|
|
Threat of new entry |
|
|
|
Buyer power |
|
|
|
Supplier power |
|
|
|
Threat of substitution |
|
|
Porter’s generic strategies
-
Once a business has applied the Five Forces model to its own circumstances, Porter recommended a range of generic strategies to increase its chances of competing
-
On the basis of cost or through differentiation
-
In the mass market or within a smaller niche market
-
-
It emphasises the importance of developing distinctive capabilities and avoid being ‘stuck in the middle’
Porter’s generic matrix

Mass market strategies
-
Cost Leadership
-
Most suitable for businesses that have a significant cost advantage over rivals
-
Cost leadership with parity is where a business has lower costs than rivals but charges the same price
-
Examples include hotel chains such as Premier Inn and Ibis Styles
-
-
Cost leadership with proximity is where a business has lower costs and charges a lower price than rivals
-
Examples include budget airlines such as Southwestern and Ryanair
-
-
-
Differentiation
-
Businesses that cannot be the most competitive on cost should make its products distinct from those of rivals
-
This allows a business to charge a premium price and achieve a high profit margin
-
Examples of businesses that adopt a mass market differentiation strategy include
-
Coca Cola, whose trusted and well-known branding includes its logo, brand colours and characters such as the Coca Cola truck
-
Samsung‘s cutting-edge mobile phones have the most advanced package of technical features in the mass market
-
Volvo‘s focus on safety and build quality allows it to charge premium prices in the mass market
-
-
Niche market strategies
-
Businesses that operate in a niche markets should adopt one of two focus strategies that closely meet the needs of its specific group of customers
-
Cost focus strategy
-
This involves being the lowest cost competitor within the market niche
-
Carnival Cruises sells cruises to locations including the Caribbean and Europe and is well-known for it’s eye-catching low fares that can be offered due to its fleet of smaller vessels that operate at full capacity
-
Glasses Direct is an online retailer of spectacles that sells popular styles of lesser-known brands at very low prices as a result of its low overhead costs
-
-
-
Differentiation focus strategy
-
A differentiation focus involves offering specialised products within the niche market
-
Hotel Chocolat sells a range of premium, fair-trade celebration confectionary in its chain of beautifully-designed retail outlets
-
Brompton Bicycle Retail sells innovative products, such as the folding bicycle, that closely meet the needs of its wealthy commuter target market
-
-
Stuck in the middle
-
Failing to adopt one of the strategies would result in being unable to compete successfully with rivals
-
A business should select its strategy and concentrate its resources on pursuing it rather than simply responding to its competitors’ actions
-
-
Pursuing a mixture of strategies is also not feasible in the long term
-
Cost leadership and differentiation are not compatible
-
Low prices combined with high quality can negatively affect consumer perceptions of the product
-
-
Evaluation of Porter’s generic strategies
|
Benefits |
Drawbacks |
|---|---|
|
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Although Porter’s Generic Strategies are not explicitly listed within this specification, it is important that you understand that Five Forces Analysis allows a business to determine its competitive strategy. For this reason it is included here.
Additionally, as Blue Ocean Strategy is an alternative to Porter’s acceptance of competitive forces in his Generic Strategies (Kim & Mauborgne consider these to be Red Ocean Strategies) it is appropriate to understand the concept.
Blue ocean strategy
-
Blue Ocean strategy is the simultaneous pursuit of differentiation and low-cost strategies
-
This opens up a new market space and creates new demand, so there is less fighting over existing demand
-
Uncontested market space is captured by products that other businesses have not yet adopted, making competition irrelevant
-
There is ample opportunity for profitable and rapid growth
-
-
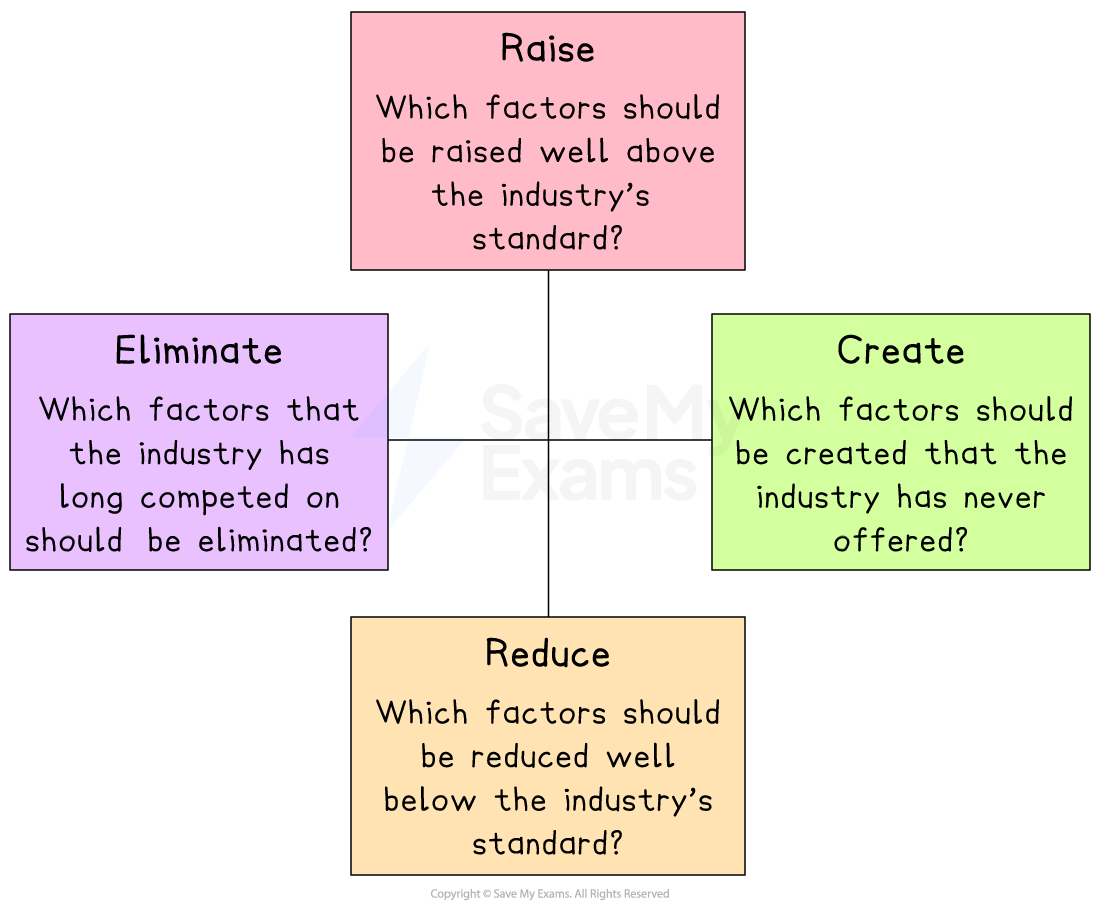
Businesses pursuing this strategy follow the Four Actions Framework to identify a new value curve which combines cost and differentiation in a new, innovative way
The four actions framework
-
The four actions in the framework are:
-
Raise
-
Question which features or products should be better than the industry standard
-
-
Create
-
Question which features or products have never existed and should be created
-
-
Reduce
-
Question which features of products should be downplayed to levels below industry standards
-
-
Eliminate
-
Question which features or products have been overcompeted and eliminate them
-
-
Case Study
Nintendo’s Blue Ocean strategy
In the early 2000s, Nintendo was struggling as industry giants Sony and Microsoft dominated the market
