Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
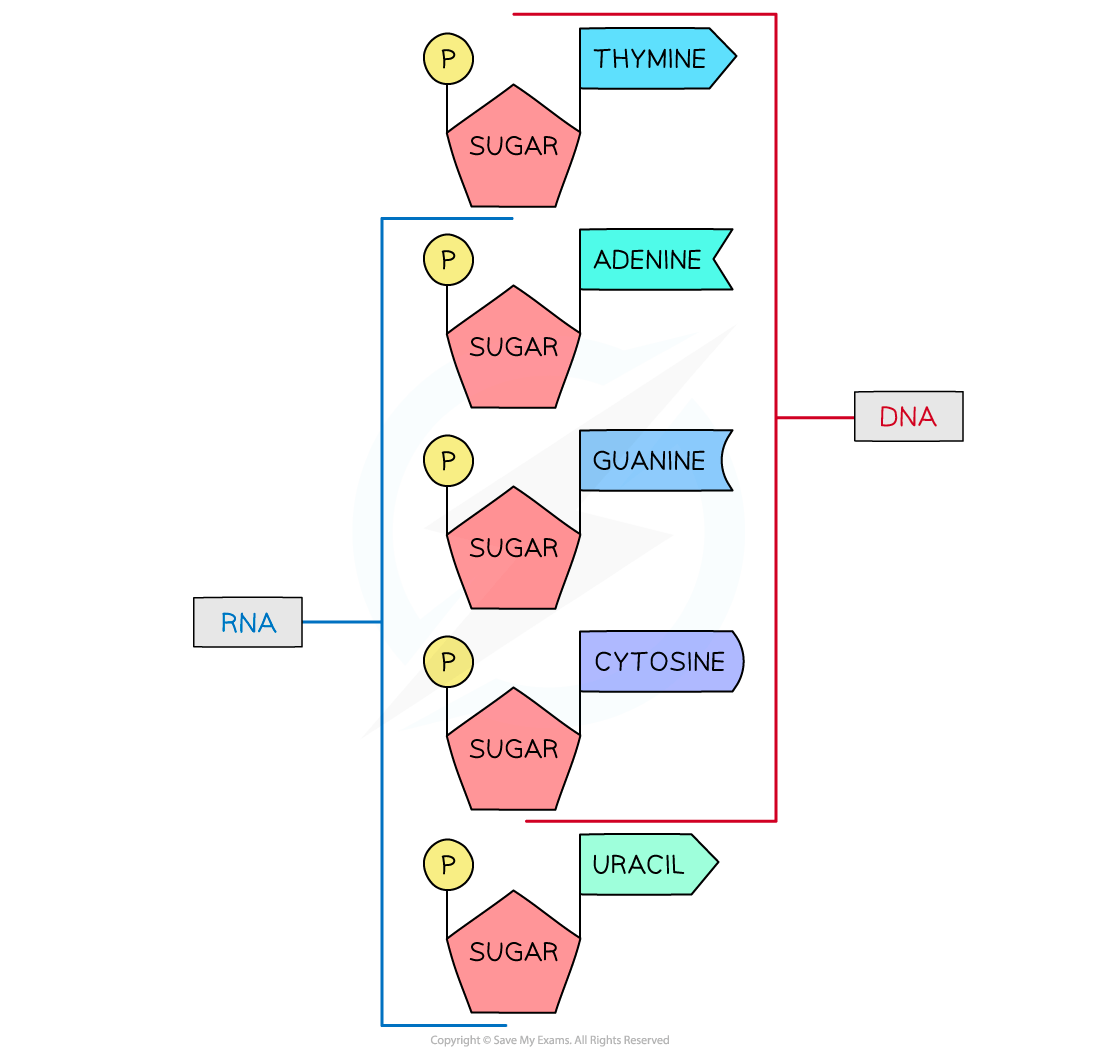
the-structure-of-rna
RNA structure
-
Like DNA:
-
The nucleic acid RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a polynucleotide
-
It is made up of many nucleotides linked together in a long chain
-
-
RNA nucleotides contain the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G) and cytosine (C)
-
-
Unlike DNA:
-
RNA nucleotides never contain the nitrogenous base thymine (T)
-
In place of this they contain the nitrogenous base uracil (U)
-
-
RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar ribose (instead of deoxyribose)
-
RNA molecules are only made up of one polynucleotide strand (they are single-stranded)
-
-
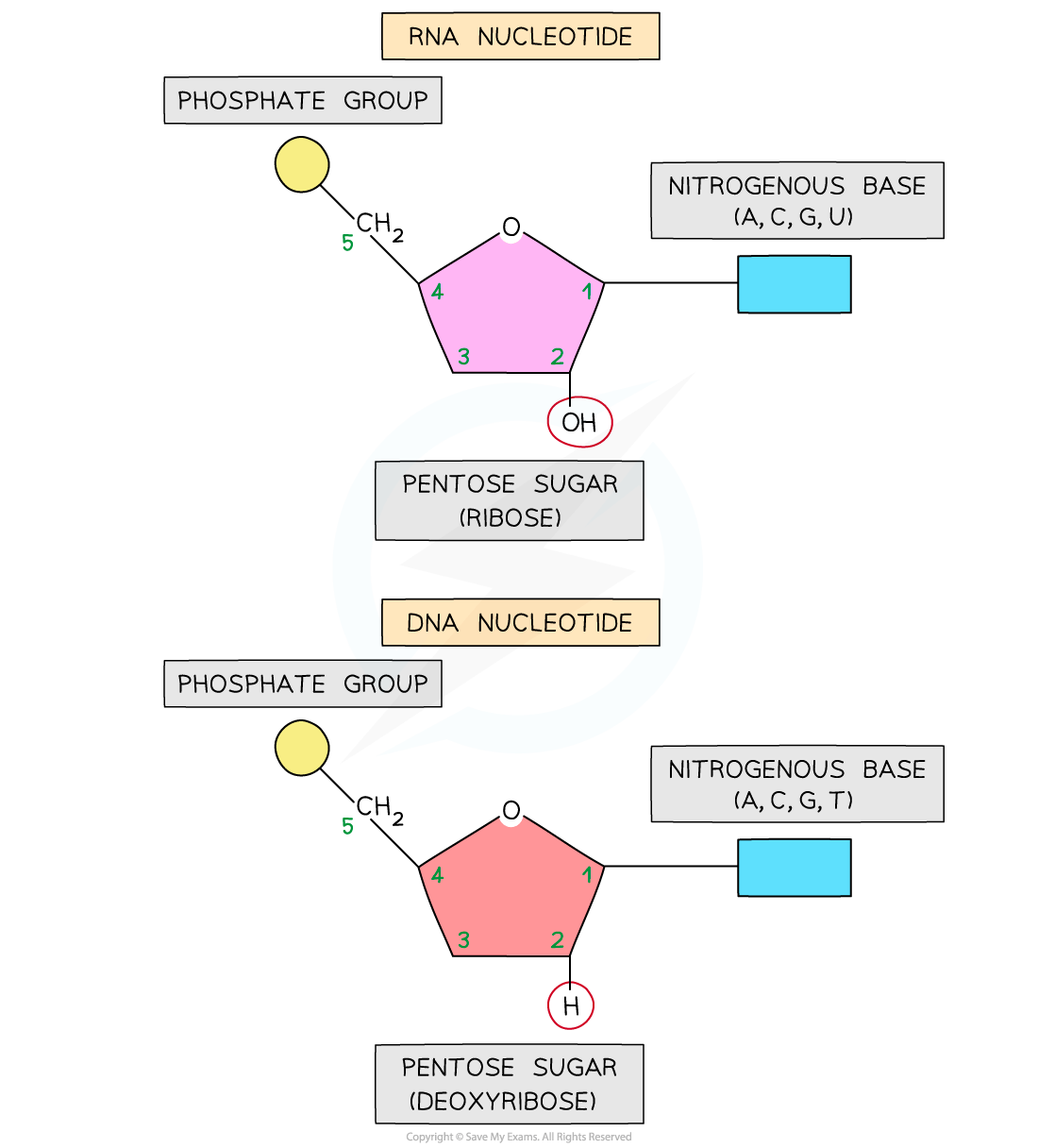
Each RNA polynucleotide strand is made up of alternating ribose sugars and phosphate groups linked together
-
The nitrogenous bases of each nucleotide projecting out sideways from the single-stranded RNA molecule
-
|
Properties |
DNA |
RNA |
|---|---|---|
|
Pentose sugar |
Deoxyribose |
Ribose |
|
Bases |
Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) |
Adenine (A) Uracil (U) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) |
|
Number of strands |
Double-stranded (double helix) |
Single-stranded |
-
The sugar-phosphate bonds (between different nucleotides in the same strand) are covalent bonds known as phosphodiester bonds
-
These bonds form what is known as the sugar-phosphate backbone of the RNA polynucleotide strand
-
The phosphodiester bonds link the 5-carbon of one ribose sugar molecule to the phosphate group from the same nucleotide, which is itself linked by another phosphodiester bond to the 3-carbon of the ribose sugar molecule of the next nucleotide in the strand
-
-
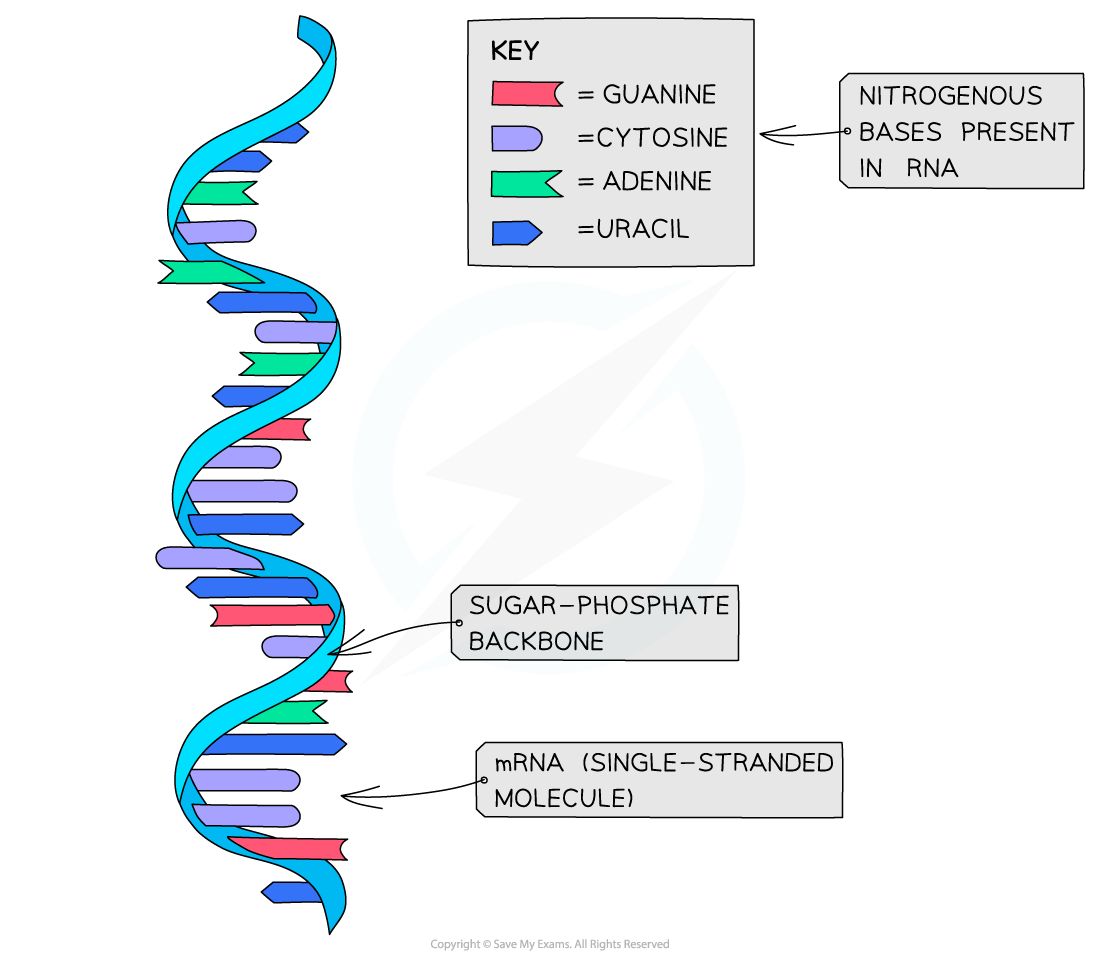
An example of an RNA molecule is messenger RNA (mRNA)
-
mRNA is the transcript copy of a gene that encodes a specific polypeptide
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You need to know the difference between DNA and RNA molecules (bases, number of strands, pentose sugar present).
