Biology_A-level_Aqa
-
1-biological-molecules
1-1-biological-molecules-carbohydrates11 主题-
1-1-1-biological-molecules-key-terms
-
1-1-2-biological-molecules-reactions
-
1-1-3-monosaccharides
-
1-1-4-glucose
-
1-1-5-the-glycosidic-bond
-
1-1-6-chromatography-monosaccharides
-
1-1-7-disaccharides
-
1-1-8-starch-and-glycogen
-
1-1-9-cellulose
-
1-1-10-biochemical-tests-sugars-and-starch
-
1-1-11-finding-the-concentration-of-glucose
-
1-1-1-biological-molecules-key-terms
-
1-2-biological-molecules-lipids3 主题
-
1-3-biological-molecules-proteins5 主题
-
1-4-proteins-enzymes12 主题
-
1-4-1-many-proteins-are-enzymes
-
1-4-2-enzyme-specificity
-
1-4-3-how-enzymes-work
-
1-4-4-required-practical-measuring-enzyme-activity
-
1-4-5-drawing-a-graph-for-enzyme-rate-experiments
-
1-4-6-using-a-tangent-to-find-initial-rate-of-reaction
-
1-4-7-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-temperature
-
1-4-8-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-ph
-
1-4-10-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-enzyme-concentration
-
1-4-11-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-substrate-concentration
-
1-4-12-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-inhibitors
-
1-4-14-control-of-variables-and-uncertainty
-
1-4-1-many-proteins-are-enzymes
-
1-5-nucleic-acids-structure-and-dna-replication8 主题
-
1-5-2-nucleotide-structure-and-the-phosphodiester-bond
-
1-5-3-dna-structure-and-function
-
1-5-4-rna-structure-and-function
-
1-5-5-ribosomes
-
1-5-6-the-origins-of-research-on-the-genetic-code
-
1-5-8-the-process-of-semi-conservative-replication
-
1-5-9-calculating-the-frequency-of-nucleotide-bases
-
1-5-10-the-watson-crick-model
-
1-5-2-nucleotide-structure-and-the-phosphodiester-bond
-
1-6-atp-water-and-inorganic-ions4 主题
-
2-cell-structure2-1-cell-structure7 主题
-
2-2-the-microscope-in-cell-studies4 主题
-
2-3-cell-division-in-eukaryotic-and-prokaryotic-cells8 主题
-
2-4-cell-membranes-and-transport7 主题
-
2-5-cell-recognition-and-the-immune-system7 主题
-
2-6-vaccines-disease-and-monoclonal-antibodies6 主题
-
3-exchange-and-transport3-1-adaptations-for-gas-exchange6 主题
-
3-2-human-gas-exchange10 主题
-
3-2-1-the-human-gas-exchange-system
-
3-2-2-dissecting-the-gas-exchange-system
-
3-2-3-microscopy-and-gas-exchange-surfaces
-
3-2-4-investigating-gas-exchange
-
3-2-5-the-alveolar-epithelium
-
3-2-6-ventilation-and-gas-exchange
-
3-2-8-the-effects-of-lung-disease
-
3-2-9-pollution-and-smoking-data
-
3-2-10-risk-factor-data
-
3-2-11-correlations-and-causal-relationships
-
3-2-1-the-human-gas-exchange-system
-
3-3-digestion-and-absorption5 主题
-
3-4-mass-transport-in-animals6 主题
-
3-5-the-circulatory-system-in-animals8 主题
-
3-6-mass-transport-in-plants6 主题
-
4-genetics-variation-and-interdependence4-1-dna-genes-and-chromosomes7 主题
-
4-2-dna-and-protein-synthesis6 主题
-
4-3-genetic-diversity-mutations-and-meiosis7 主题
-
4-4-genetic-diversity-and-adaptation6 主题
-
4-5-species-and-taxonomy4 主题
-
4-6-biodiversity9 主题
-
5-energy-transfers-in-and-between-organisms-a-level-only5-1-photosynthesis-a-level-only5 主题
-
5-2-respiration-a-level-only7 主题
-
5-3-energy-and-ecosystems-a-level-only9 主题
-
5-4-nutrient-cycles-a-level-only4 主题
-
6-organisms-respond-to-changes-in-their-environments-a-level-only6-1-response-to-stimuli-a-level-only12 主题
-
6-1-1-survival-and-response
-
6-1-2-growth-factors-in-flowering-plants
-
6-1-3-indoleacetic-acid-iaa
-
6-1-4-taxes-and-kinesis
-
6-1-5-reflex-arcs
-
6-1-6-required-practical-investigating-animal-movement
-
6-1-7-the-pacinian-corpuscle
-
6-1-8-pacinian-corpuscles-generator-potential
-
6-1-9-investigating-touch-and-temperature-receptors
-
6-1-10-the-human-retina
-
6-1-11-myogenic-stimulation-of-the-heart
-
6-1-13-heart-rate
-
6-1-1-survival-and-response
-
6-2-nervous-coordination-a-level-only10 主题
-
6-3-skeletal-muscles-a-level-only6 主题
-
6-4-homeostasis-a-level-only11 主题
-
6-4-1-principles-of-homeostasis
-
6-4-2-negative-feedback
-
6-4-3-glucose-concentration-and-insulin
-
6-4-4-glucose-regulation-glucagon
-
6-4-5-glucose-regulation-adrenaline
-
6-4-6-glucose-regulation-the-liver
-
6-4-7-diabetes
-
6-4-8-required-practical-determining-the-concentration-of-glucose-in-urine
-
6-4-9-nephron-structure
-
6-4-10-nephron-function
-
6-4-11-control-of-blood-water-potential
-
6-4-1-principles-of-homeostasis
-
7-genetics-populations-evolution-and-ecosystems-a-level-only7-1-inheritance-a-level-only6 主题
-
7-2-populations-a-level-only3 主题
-
7-3-evolution-a-level-only5 主题
-
7-4-populations-in-ecosystems-a-level-only7 主题
-
8-the-control-of-gene-expression-a-level-only8-1-genetic-mutations-a-level-only2 主题
-
8-2-regulation-of-gene-expression-a-level-only11 主题
-
8-2-1-totipotent-cells
-
8-2-2-stem-cells
-
8-2-3-the-use-of-stem-cells
-
8-2-4-producing-tissue-cultures-of-explants
-
8-2-5-regulation-of-transcription
-
8-2-6-evaluating-data-about-genetic-expression
-
8-2-7-epigenetics
-
8-2-8-epigenetics-and-disease
-
8-2-9-rna-interference
-
8-2-10-two-types-of-tumours
-
8-2-11-tumour-development
-
8-2-1-totipotent-cells
-
8-3-using-genome-projects-a-level-only4 主题
-
8-4-gene-technologies-a-level-only13 主题
-
8-4-1-recombinant-dna-technology
-
8-4-2-producing-fragments-of-dna
-
8-4-3-investigating-the-specificity-of-restriction-enzymes
-
8-4-4-polymerase-chain-reaction
-
8-4-5-culture-of-transformed-host-cells
-
8-4-6-uses-of-recombinant-dna-technology
-
8-4-7-dna-probes-and-dna-hybridisation
-
8-4-8-screening-patients
-
8-4-9-genetic-counselling-and-personalised-medicine
-
8-4-10-variable-number-tandem-repeats
-
8-4-11-gel-electrophoresis
-
8-4-12-genetic-fingerprinting
-
8-4-13-uses-of-genetic-fingerprinting
-
8-4-1-recombinant-dna-technology
-
exam-guidance-and-skillsessay-guidance3 主题
7-4-7-growth-rate-of-microorganisms
Investigating growth rate using turbidity measurements
-
The population growth rate of microorganisms, such as bacteria or yeast, can be investigated by growing the microorganisms in a broth culture
-
The turbidity of the suspension can then be used as a way of estimating the number of cells (i.e. the population size) of the microorganisms in the broth culture
-
Turbidity is simply a measure of the cloudiness of a suspension (i.e. how much light can pass through it)
-
-
As the microorganisms in the broth culture reproduce and their population grows, the suspension becomes progressively more turbid (cloudy)
-
This changing turbidity can be monitored by measuring how much light can pass through the suspension at fixed time intervals after the initial inoculation of the nutrient broth with the microorganisms
-
A turbidity meter, a light sensor or a colorimeter (connected to a datalogger) can be used to take these measurements
-
-
The results can then be used to plot a population growth curve to show how the population of microorganism grew over time
Using logarithms when investigating bacteria
-
Bacterial colonies can grow at rapid rates when in culture, with very large numbers of bacteria produced within hours
-
Dealing with the experimental data relating to large numbers of bacteria can be difficult when using traditional linear scales
-
There is a wide range of very small and very large numbers
-
This makes it hard to work out a suitable scale for the axes of graphs
-
-
Logarithmic scales can be very useful when investigating bacteria
What is a logarithmic scale?
-
A log scale doesn’t increase by equal amounts like 100, 200, 300
-
Instead, it increases by powers of 10:
-
102=100
-
103=1000
-
-
This allows large changes in data (e.g. population size) to be shown on a compressed axis
-
You can recognise a log scale because the intervals on the y-axis are not evenly spaced
Reading a log scale
-
Logarithmic scales allow a wide range of values to be shown on one graph
-
To read from the logarithmic scale, you should consider the following:
-
Identify the powers of 10 on the log scale
-
For example: 10¹ = 10, 10² = 100, 10³ = 1000
-
-
Check the spacing
-
On a log scale, the spacing between powers of 10 is even, but the actual numbers between them are not linear
-
This means 100 to 1000 is broken into log-based steps, not 200, 300, etc.
-
-
Estimate values between powers of 10
-
Use known log₁₀ values:
-
100 → log₁₀ = 2
-
320 → log₁₀ ≈ 2.5
-
1000 → log₁₀ = 3
-
-
For a value like 320, find the point halfway between 100 and 1000 on the log axis
-
-
Use a calculator for precision
-
Type log(value) into your calculator to find its position on the scale
-
E.g. log(320) ≈ 2.5, so it’s slightly over halfway between 100 and 1000
-
-
Read carefully
-
Never assume even spacing = even number gaps
-
Always estimate based on logarithmic spacing
-
-
Example: reading a logarithmic scale
-
In this example, two graphs show population growth for a microbial population
-
The first uses a linear scale
-
The second uses a logarithmic scale
-
-
At 5 hours, the population size is 320
-
Annotations on each graph show how this reading was taken
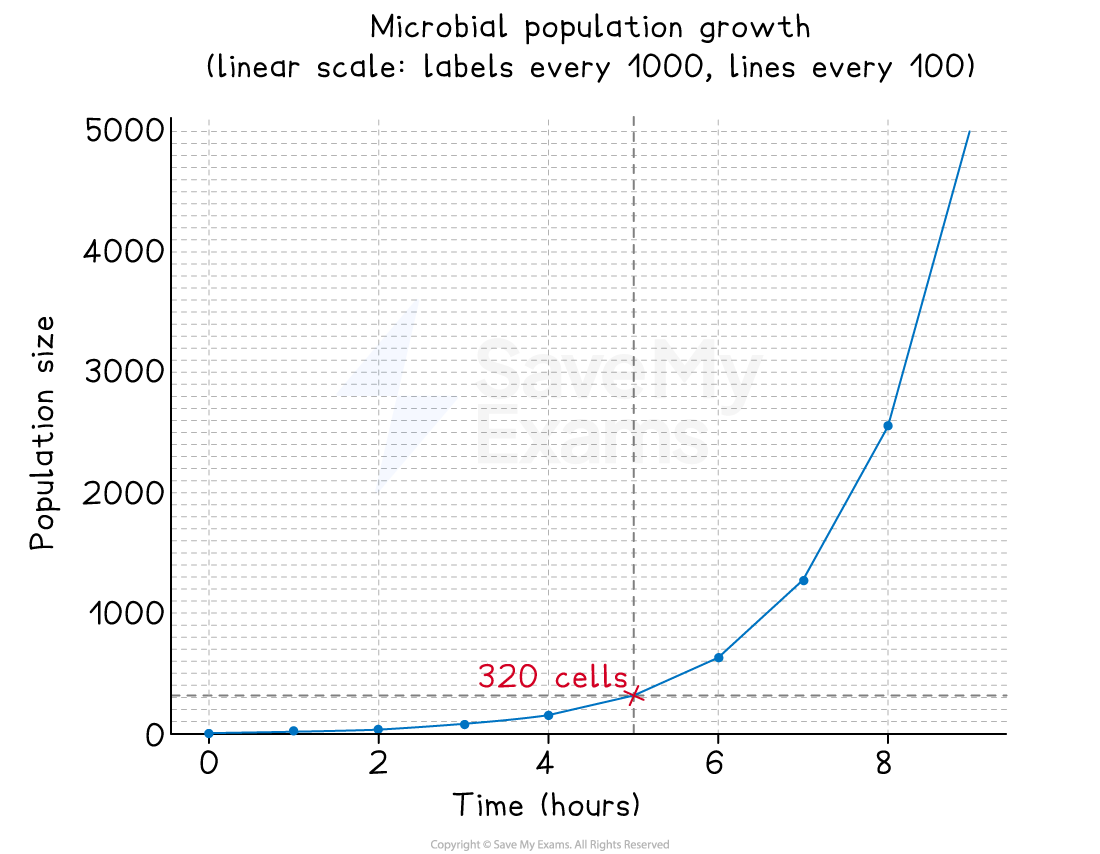
A linear graph used to show population growth. Annotations show the reading of population size at 5 hours.
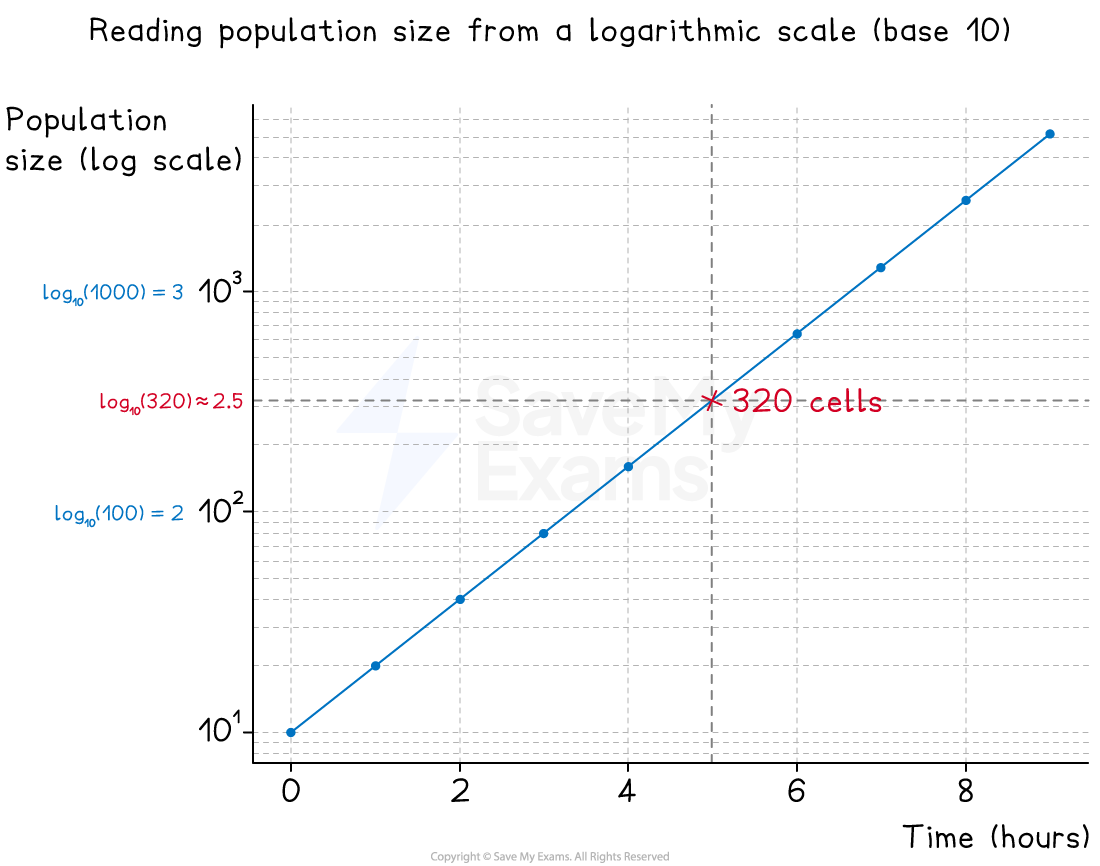
A log graph used to show population growth. Annotations show the reading of population size at 5 hours. -
pH scales
-
The pH scale is logarithmic
-
The concentration of hydrogen ions varies massively between each pH level
-

Examiner Tips and Tricks
You won’t be expected to convert values into logarithms or create a log scale graph in the exam. Instead, you might be asked to interpret results that use logarithmic scales or explain the benefit of using one!
Remember that graphs with a logarithmic scale have uneven intervals between values on one or more axes.
